Thrombosis in COVID-19
- PMID: 32857878
- PMCID: PMC7674272
- DOI: 10.1002/ajh.25982
Thrombosis in COVID-19
Abstract
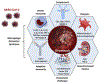
Thrombotic complications are frequent in COVID-19 and contribute significantly to mortality and morbidity. We review several mechanisms of hypercoagulability in sepsis that may be upregulated in COVID-19. These include immune-mediated thrombotic mechanisms, complement activation, macrophage activation syndrome, antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, hyperferritinemia, and renin-angiotensin system dysregulation. We highlight biomarkers within each pathway with potential prognostic value in COVID-19. Lastly, recent observational studies have evaluated a role for the expanded use of therapeutic anticoagulation in COVID-19. We review strengths and weaknesses of these studies, and we also discuss the hypothetical benefit and anticipated challenges of fibrinolytic therapy in COVID-19.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures


References
-
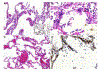
- Wichmann D, Sperhake J-P, Lütgehetmann M, Steurer S, Edler C, Heinemann A, Heinrich F, Mushumba H, Kniep I, Schröder AS, Burdelski C, Heer G de, Nierhaus A, Frings D, Pfefferle S, Becker H, Bredereke-Wiedling H, Weerth A de, Paschen H-R, Sheikhzadeh-Eggers S, Stang A, Schmiedel S, Bokemeyer C, Addo MM, Aepfelbacher M, Püschel K, Kluge S. Autopsy Findings and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients With COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann Intern Med 2020. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
