Effects of the Preschool-Based Family-Involving DAGIS Intervention Program on Children's Energy Balance-Related Behaviors and Self-Regulation Skills: A Clustered Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 32859118
- PMCID: PMC7551940
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12092599
Effects of the Preschool-Based Family-Involving DAGIS Intervention Program on Children's Energy Balance-Related Behaviors and Self-Regulation Skills: A Clustered Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
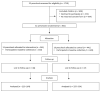
The study examines the effects of a preschool-based family-involving multicomponent intervention on children's energy balance-related behaviors (EBRBs) such as food consumption, screen time and physical activity (PA), and self-regulation (SR) skills, and whether the intervention effects differed among children with low or high parental educational level (PEL) backgrounds. The Increased Health and Wellbeing in Preschools (DAGIS) intervention was conducted as a clustered randomized controlled trial, clustered at preschool level, over five months in 2017-2018. Altogether, 802 children aged 3-6 years in age participated. Parents reported children's consumption of sugary everyday foods and beverages, sugary treats, fruits, and vegetables by a food frequency questionnaire, and screen time by a 7-day diary. Physical activity was assessed by a hip-worn accelerometer. Cognitive and emotional SR was reported in a questionnaire by parents. General linear mixed models with and without repeated measures were used as statistical methods. At follow-up, no differences were detected in EBRBs or SR skills between the intervention and control group, nor did differences emerge in children's EBRBs between the intervention and the control groups when stratified by PEL. The improvement in cognitive SR skills among low PEL intervention children differed from low PEL control children, the significance being borderline. The DAGIS multicomponent intervention did not significantly affect children's EBRBs or SR. Further sub-analyses and a comprehensive process evaluation may shed light on the non-significant findings.
Keywords: children; energy balance-related behaviors; intervention effects; intervention mapping; multicomponent intervention; parental educational level; preschoolers; randomized controlled trial; self-regulation skills.
Conflict of interest statement
L.K. is a board member of the company TwoDads. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Report of the Comission on Ending Childhood Obesity. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- Mantziki K., Vassilopoulos A., Radulian G., Borys J.-M., Du Plessis H., Gregorio M.J., Graca P., De Henauw S., Handjiev S., Visscher T. Inequities in Energy-Balance Related Behaviours and Family Environmental Determinants in European Children: Baseline Results of the Prospective EPHE Evaluation Study. BMC Public Health. 2015;15:1203. doi: 10.1186/s12889-015-2540-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

