Association of miR-125b, miR-17 and let-7c Dysregulations With Response to Anti-epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibodies in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 32859639
- PMCID: PMC7472450
- DOI: 10.21873/cgp.20217
Association of miR-125b, miR-17 and let-7c Dysregulations With Response to Anti-epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibodies in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Background/aim: MicroRNAs (miRs) play an important role in the regulation of cancer-related processes and are promising candidates for cancer biomarkers. The aim of the study was to evaluate the association of response to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) with selected miR expression profiles, including miR-125b, let-7c, miR-99a, miR-17, miR-143 and miR-145 in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients.
Patients and methods: This retrospective study included 46 patients with mCRC harbouring wild-type RAS gene treated with cetuximab or panitumumab combined with chemotherapy in first- or second-line therapy. The miR expression was assessed using qRT-PCR.
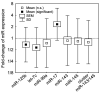
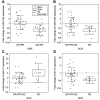
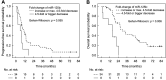
Results: Down-regulation of miR-125b and let-7c and up-regulation of miR-17 were found in the tumour tissue (p=0.0226, p=0.0040, p<0.0001). Objective response rate (ORR) was associated with up-regulation of miR-125b (p=0.0005). Disease control rate (DCR) was associated with up-regulation of miR-125b and let-7c (p=0.0383 and p=0.0255) and down-regulation of miR-17 (p=0.0464). MiR-125b showed correlation with progression-free and overall survival (p=0.055 and p=0.006).
Conclusion: The results show that up-regulation of miR-125b is associated with higher ORR and DCR and longer survival; let-7c up-regulation and miR-17 down-regulation are associated with higher DCR in mCRC patients treated with anti-EGFR mAbs.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; cetuximab; chemotherapy; let-7c; miR-125b; miR-17; microRNA; panitumumab.
Copyright© 2020, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
OF received honoraria from Roche, GSK and Pfizer for consultations and lectures unrelated to this project. JF has received honoraria from Astra Zeneca, Roche and Novartis for consultations and lectures unrelated to this project. OS, PH, VL, OV, JB, RK, OT, DM and PP declare that they have no actual or potential conflict of interest including any financial, personal or other relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence this work.
Figures
References
-
- Lièvre A, Bachet JB, Le Corre D, Boige V, Landi B, Emile JF, Côté JF, Tomasic G, Penna C, Ducreux M, Rougier P, Penault-Llorca F, Laurent-Puig P. KRAS mutation status is predictive of response to cetuximab therapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66(8):3992–3995. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0191. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Karapetis CS, Khambata-Ford S, Jonker DJ, O’Callaghan CJ, Tu D, Tebbutt NC, Simes RJ, Chalchal H, Shapiro JD, Robitaille S, Price TJ, Shepherd L, Au HJ, Langer C, Moore MJ, Zalcberg JR. K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(17):1757–1765. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0804385. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Freeman DJ, Juan T, Sikorski R, Suggs S, Radinsky R, Patterson SD, Chang DD. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(10):1626–1634. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.7116. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lièvre A, Bachet JB, Boige V, Cayre A, Le Corre D, Buc E, Ychou M, Bouché O, Landi B, Louvet C, André T, Bibeau F, Diebold MD, Rougier P, Ducreux M, Tomasic G, Emile JF, Penault-Llorca F, Laurent-Puig P. KRAS mutations as an independent prognostic factor in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(3):374–379. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.12.5906. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
