Model-Based Meta-Analysis Compares DAS28 Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Effects and Suggests an Expedited Trial Design for Early Clinical Development
- PMID: 32860421
- PMCID: PMC7894503
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.2023
Model-Based Meta-Analysis Compares DAS28 Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Effects and Suggests an Expedited Trial Design for Early Clinical Development
Abstract
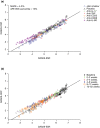
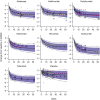
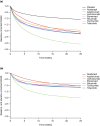
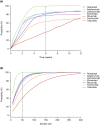
A nonlinear mixed effects modeling approach was used to conduct a model-based meta-analysis (MBMA) of longitudinal, summary-level, baseline-corrected 28-joint Disease Activity Score (ΔDAS28) clinical trial data from seven approved rheumatoid arthritis (RA) drugs (abatacept, adalimumab, certolizumab, etanercept, rituximab, tocilizumab, and tofacitinib), representing 130 randomized clinical trials in 27,355 patients. All of the drugs except tocilizumab were found to have relatively similar ΔDAS28 time courses and efficacy (baseline-corrected and placebo-corrected) at 24 weeks and beyond of approximately 0.87-1.3 units in the typical RA patient population. Tocilizumab was estimated to have a differentially greater response of 1.99 at 24 weeks, likely due to its disproportionate effect on the acute-phase cytokine interleukin-6. Baseline DAS28, disease duration, percentage of male participants, and the year of conduct of the trial were found to have statistically significant effects on the timing and/or magnitude of ΔDAS28 in the control arms. Clinical trial simulations using the present MBMA indicated that abatacept, certolizumab, etanercept, tocilizumab, and tofacitinib would be expected to have a greater than 70% probability of showing a statistically significant difference vs. control at Week 6 with a sample size of ~ 30 patients per arm. In future RA clinical trials, an interim analysis conducted as early as 6 weeks after treatment initiation, with relatively small sample sizes, should be sufficient to detect the ΔDAS28 treatment effect vs. placebo.
© 2020 Bristol-Myers Squibb. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of Bristol Myers Squibb and hold company stock.
Figures
References
-
- McInnes, I.B. & Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 2205–2219 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Prevoo, M.L. , van't Hof, M.A. , Kuper, H.H. , van Leeuwen, M.A. , van de Putte, L.B. & van Riel, P.L. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty‐eight‐joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 38, 44–48 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Fransen, J. & van Riel, P.L.C.M. The disease activity score and the EULAR response criteria. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 35, 745–757, vii‐viii (2009). - PubMed
-
- van der Heijde, D.M. , van 't Hof, M. , van Riel, P.L. , & van de Putte, L.B. Development of a disease activity score based on judgment in clinical practice by rheumatologists. J. Rheumatol. 20, 579–581 (1993). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

