A High-Throughput Assay for Circulating Antibodies Directed Against the S Protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
- PMID: 32860510
- PMCID: PMC7499578
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa531
A High-Throughput Assay for Circulating Antibodies Directed Against the S Protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Abstract
More than 24 million infections with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) were confirmed globally by September 2020. While polymerase chain reaction-based assays are used for diagnosis, there is a need for high-throughput, rapid serologic methods. A Luminex binding assay was developed and used to assess simultaneously the presence of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-specific antibodies in human serum and plasma. Clear differentiation was achieved between specimens from infected and uninfected subjects, and a wide range of serum/plasma antibody levels was delineated in infected subjects. All 25 specimens from 18 patients with COVID-19 were positive in the assays with both the trimeric spike and the receptor-binding domain proteins. None of the 13 specimens from uninfected subjects displayed antibodies to either antigen. There was a highly statistically significant difference between the antibody levels of COVID-19-infected and -uninfected specimens (P < .0001). This high-throughput antibody assay is accurate, requires only 2.5 hours, and uses 5 ng of antigen per test.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibodies; antibody assay; coronavirus.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


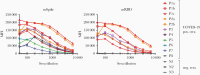
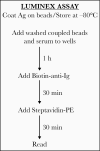
Update of
-
A High Through-put Assay for Circulating Antibodies Directed against the S Protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Corona virus 2.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Apr 17:2020.04.14.20059501. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.14.20059501. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: J Infect Dis. 2020 Oct 13;222(10):1629-1634. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa531. PMID: 32511609 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Storch GA. Diagnostic virology. Clin Infect Dis 2000; 31:739–51. - PubMed
-
- National Museum of American History–Behring Collection. The antibody initiative: diagnosing disease with antibodies Available at: https://americanhistory.si.edu/collections/object-groups/antibody-initia.... Accessed 10 August 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

