Esketamine Nasal Spray for Rapid Reduction of Depressive Symptoms in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder Who Have Active Suicide Ideation With Intent: Results of a Phase 3, Double-Blind, Randomized Study (ASPIRE II)
- PMID: 32861217
- PMCID: PMC7816667
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa068
Esketamine Nasal Spray for Rapid Reduction of Depressive Symptoms in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder Who Have Active Suicide Ideation With Intent: Results of a Phase 3, Double-Blind, Randomized Study (ASPIRE II)
Abstract
Background: Patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) having active suicidal ideation with intent require immediate treatment.
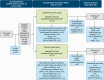
Methods: This double-blind study (ASPIRE II) randomized adults (aged 18-64 years) with MDD having active suicidal ideation with intent to esketamine 84 mg or placebo nasal spray twice weekly for 4 weeks, given with comprehensive standard of care (hospitalization ≥5 days and newly initiated or optimized oral antidepressant[s]). Change from baseline to 24 hours post-first dose in Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale total score (primary efficacy endpoint) was analyzed using ANCOVA. Clinical Global Impression-Severity of Suicidality-revised (key secondary endpoint) was analyzed using ANCOVA on ranks of change.
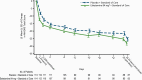
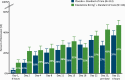
Results: Of 230 patients who were randomized (115 per arm), 227 received study drug and were included in efficacy/safety analyses; 184 (80.0%) completed double-blind treatment. Greater improvement in Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale total score was observed with esketamine (mean [SD]: -15.7 [11.56]) vs placebo (-12.4 [10.43]), each with standard of care, at 24 hours (least-squares mean difference [SE]: -3.9 [1.39], 95% CI: -6.60, -1.11; 2-sided P = .006). This was also noted at the earlier (4-hour) timepoint (least-squares mean difference -4.2, 95% CI: -6.38, -1.94). Patients in both treatment groups experienced rapid reduction in Clinical Global Impression-Severity of Suicidality-revised score; the between-group difference was not statistically significant. The most common adverse events among esketamine-treated patients were dizziness, dissociation, nausea, dysgeusia, somnolence, headache, and paresthesia.
Conclusion: This study confirmed rapid and robust reduction of depressive symptoms with esketamine nasal spray in severely ill patients with MDD who have active suicidal ideation with intent. Trial Registration: Clinical Trials.gov identifier: NCT03097133.
Keywords: Esketamine; depression; suicidal ideation; suicide risk.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures

References
-
- Alphs L, Fu D-J, Williamson D, Turkoz I, Jamieson C, Revicki D, Canuso CM (2020) Suicide ideation and behavior assessment tool (SIBAT): evaluation of intra- and inter-rater reliability, validity, and mapping to Columbia Classification Algorithm of Suicide Assessment. Psychiatry Research; (in press), 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113495. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2003) Practice guideline for the assessment and treatment of patients with suicidal behaviors. Am J Psychiatry 160 (11Suppl):1–60. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5) 5th ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
-
- Blair-West GW, Cantor CH, Mellsop GW, Eyeson-Annan ML (1999) Lifetime suicide risk in major depression: sex and age determinants. J Affect Disord 55:171–178. - PubMed
-
- Bremner JD, Krystal JH, Putnam FW, Southwick SM, Marmar C, Charney DS, Mazure CM (1998) Measurement of dissociative states with the Clinician-Administered Dissociative States Scale (CADSS). J Trauma Stress 11:125–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

