Burden of diabetes mellitus and its impact on COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis of real-world evidence
- PMID: 32862098
- PMCID: PMC7439970
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.08.014
Burden of diabetes mellitus and its impact on COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis of real-world evidence
Abstract
Background & aims: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) spreads rapidly and within no time, it has been declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization. Evidence suggests diabetes to be a risk factor for the progression and poor prognosis of COVID-19. Therefore, we aimed to understand the pooled prevalence of diabetes in patients infected with COVID-19. We also aimed to compute the risk of mortality and ICU admissions in COVID-19 patients with and without diabetes.
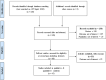
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was performed in PubMed to identify the articles reporting the diabetes prevalence and risk of mortality or ICU admission in COVID-19 patients. The primary outcome was to compute the pooled prevalence of diabetes in COVID-19 patients. Secondary outcomes included risk of mortality and ICU admissions in COVID-19 patients with diabetes compared to patients without diabetes.
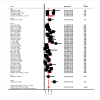
Results: This meta-analysis was based on a total of 23007 patients from 43 studies. The pooled prevalence of diabetes in patients infected with COVID-19 was found to be 15% (95% CI: 12%-18%), p = <0.0001. Mortality risk was found to be significantly higher in COVID-19 patients with diabetes as compared to COVID-19 patients without diabetes with a pooled risk ratio of 1.61 (95% CI: 1.16-2.25%), p = 0.005. Likewise, risk of ICU admission rate was significantly higher in COVID-19 patients with diabetes as compared to COVID-19 patients without diabetes with a pooled risk ratio of 1.88 (1.20%-2.93%), p = 0.006.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis found a high prevalence of diabetes and higher mortality and ICU admission risk in COVID-19 patients with diabetes.
Keywords: COVID-19; Diabetes; ICU admission; Meta-analysis; Mortality; Prevalence.
Copyright © 2020 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

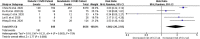
References
-
- Drosten C., Günther S., Preiser W., Van Der Werf S., Brodt H.-R., Becker S. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1967–1976. - PubMed
-
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) situation report-168. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2... Available at:
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

