Observer agreement and clinical significance of chest CT reporting in patients suspected of COVID-19
- PMID: 32862289
- PMCID: PMC7456359
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-07126-8
Observer agreement and clinical significance of chest CT reporting in patients suspected of COVID-19
Abstract
Objectives: To assess interobserver agreement and clinical significance of chest CT reporting in patients suspected of COVID-19.
Methods: From 16 to 24 March 2020, 241 consecutive patients addressed to hospital for COVID-19 suspicion had both chest CT and SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR. Eight observers (2 thoracic and 2 general senior radiologists, 2 junior radiologists, and 2 emergency physicians) retrospectively categorized each CT into one out of 4 categories (evocative, compatible for COVID-19 pneumonia, not evocative, and normal). Observer agreement for categorization between all readers and pairs of readers with similar experience was evaluated with the Kappa coefficient. The results of a consensus categorization were correlated to RT-PCR.
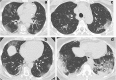
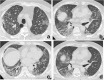
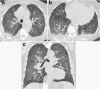
Results: Observer agreement across the 4 categories was good between all readers (κ value 0.61 95% CI 0.60-0.63) and moderate to good between pairs of readers (0.54-0.75). It was very good (κ 0.81 95% CI 0.79-0.83), fair (κ 0.32 95% CI 0.29-0.34), moderate (κ 0.56 95% CI 0.54-0.58), and moderate (0.58 95% CI 0.56-0.61) for the categories evocative, compatible, not evocative, and normal, respectively. RT-PCR was positive in 97%, 50%, 31%, and 11% of cases in the respective categories. Observer agreement was lower (p < 0.001) and RT-PCR positive cases less frequently categorized evocative in the presence of an underlying pulmonary disease (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Interobserver agreement for chest CT reporting using categorization of findings is good in patients suspected of COVID-19. Among patients considered for hospitalization in an epidemic context, CT categorized evocative is highly predictive of COVID-19, whereas the predictive value of CT decreases between the categories compatible and not evocative.
Key points: • In patients suspected of COVID-19, interobserver agreement for chest CT reporting into categories is good, and very good to categorize CT "evocative." • Chest CT can participate in estimating the likelihood of COVID-19 in patients presenting to hospital during the outbreak, CT categorized "evocative" being highly predictive of the disease whereas almost a third of patients with CT "not evocative" had a positive RT-PCR in our study. • Observer agreement is lower and CTs of positive RT-PCR cases less frequently "evocative" in presence of an underlying pulmonary disease.
Keywords: Coronavirus infections; Pneumonia; Tomography, X-ray computed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures
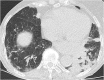
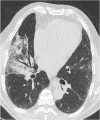
References
-
- World Health Organization (2020) Director General’s speeches. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re.... Accessed 27 Apr 2020
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

