Altered Cardiovascular Defense to Hypotensive Stress in the Chronically Hypoxic Fetus
- PMID: 32862711
- PMCID: PMC7480941
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15384
Altered Cardiovascular Defense to Hypotensive Stress in the Chronically Hypoxic Fetus
Abstract
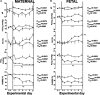
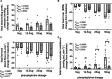
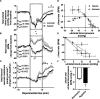
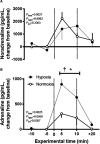
The hypoxic fetus is at greater risk of cardiovascular demise during a challenge, but the reasons behind this are unknown. Clinically, progress has been hampered by the inability to study the human fetus non-invasively for long period of gestation. Using experimental animals, there has also been an inability to induce gestational hypoxia while recording fetal cardiovascular function as the hypoxic pregnancy is occurring. We use novel technology in sheep pregnancy that combines induction of controlled chronic hypoxia with simultaneous, wireless recording of blood pressure and blood flow signals from the fetus. Here, we investigated the cardiovascular defense of the hypoxic fetus to superimposed acute hypotension. Pregnant ewes carrying singleton fetuses surgically prepared with catheters and flow probes were randomly exposed to normoxia or chronic hypoxia from 121±1 days of gestation (term ≈145 days). After 10 days of exposure, fetuses were subjected to acute hypotension via fetal nitroprusside intravenous infusion. Underlying in vivo mechanisms were explored by (1) analyzing fetal cardiac and peripheral vasomotor baroreflex function; (2) measuring the fetal plasma catecholamines; and (3) establishing fetal femoral vasoconstrictor responses to the α1-adrenergic agonist phenylephrine. Relative to controls, chronically hypoxic fetal sheep had reversed cardiac and impaired vasomotor baroreflex function, despite similar noradrenaline and greater adrenaline increments in plasma during hypotension. Chronic hypoxia markedly diminished the fetal vasopressor responses to phenylephrine. Therefore, we show that the chronically hypoxic fetus displays markedly different cardiovascular responses to acute hypotension, providing in vivo evidence of mechanisms linking its greater susceptibility to superimposed stress.
Keywords: blood pressure; fetus; hypotension; pregnancy; sheep.
Conflict of interest statement
License agreement 100395 CamDAS: Technology for simultaneous wireless recording of arterial blood pressure and blood flow in large animals. D.A. Giussani, Maastricht Instruments, The British Heart Foundation and Cambridge Enterprise. The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures

References
-
- Rudolph AM, Itskovitz J, Iwamoto H, Reuss ML, Heymann MA. Fetal cardiovascular responses to stress. Semin Perinatol 19815109–121 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

