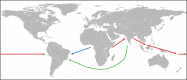
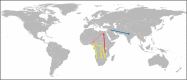
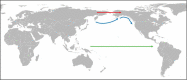
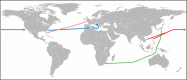
The spreading of parasites by human migratory activities
- PMID: 32862777
- PMCID: PMC7549983
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1809963
The spreading of parasites by human migratory activities
Abstract
The global spread of parasites is unquestionably linked with human activities. Migration in all its different forms played a major role in the introduction of parasites into new areas. In ancient times, mass migrations were the main causes for the spread of parasites while in the recent past and present, emigration, immigration, displacement, external and internal migration, and labor migration were the reasons for the dispersal of parasites. With the advent of seagoing ships, long-distance trading became another important mode of spreading parasites. This review summarizes the spread of parasites using notable examples. In addition, the different hypotheses explaining the arrival of Plasmodium vivax and soil-transmitted helminths in pre-Columbian America are also discussed.
Keywords: Protozoan parasites; arthropods; helminths; migration; range expansion; spread; trade.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Reinhard KJ. Archaeoparasitology in North America. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1990;82:145–163. - PubMed
-
- Hugot J-P, Reinhard KJ, Gardner SL, et al. Human enterobiasis in evolution: origin, specificity and transmission. Parasite. 1999;6:201–208. - PubMed
-
- Araújo A, Reinhard KJ, Ferreira LF, et al. Parasites as probes for prehistoric human migrations? Trends Parasitol. 2008;24:112–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous