Inhaled and systemic heparin as a repurposed direct antiviral drug for prevention and treatment of COVID-19
- PMID: 32863274
- PMCID: PMC7687307
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmed.2020-0351
Inhaled and systemic heparin as a repurposed direct antiviral drug for prevention and treatment of COVID-19
Abstract
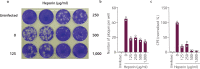
Here, we advocate a highly favourable opportunity for the treatment of COVID-19 disease by repurposing a long-serving medical agent with an excellent history of clinical use, namely heparin. Heparin is best known as an anticoagulant, but it also exhibits direct antiviral activity against many enveloped viruses and has anti-inflammatory activity. The high incidence of thromboembolic events in COVID-19 patients suggests that coagulopathy plays an important role in the SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. This already makes heparin a unique, potentially curative agent that can be used immediately to help resolve the ongoing crisis associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease. We demonstrate here in vitro that heparin does indeed inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection. The three concurrent modes of activity of heparin (antiviral, anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory) against SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 form a unique therapeutic combination. Thus, repurposing of heparin to fight SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 appears to be a powerful, readily available measure to address the current pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Inhalation; SARS-CoV-2; heparin; pulmonary coagulation.
© 2020 Royal College of Physicians 2020. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Wadman M, Couzin-Frankel J, Kaiser J, Matacic C. A rampage through the body. Science 2020; 368:356–60. - PubMed
-
- Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - Preliminary Report. N Engl J Med 2020, in press ( 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764). - PubMed
-
- Pushpakom S, Iorio F, Eyers PA, et al. Drug repurposing: progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 2019;18:41–58. - PubMed
-
- Li G, De Clercq E. Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Nat Rev Drug Discov 2020;19:149–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

