The macroeconomic effects of lockdown policies
- PMID: 32863463
- PMCID: PMC7442895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpubeco.2020.104260
The macroeconomic effects of lockdown policies
Abstract
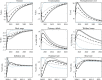
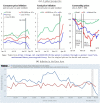
A tractable incomplete-market model with endogenous unemployment risk, sticky prices, real wage rigidity and a fiscal side is calibrated to Euro Area countries and used to analyze the macroeconomic effects of lockdown policies. Modeling them as a shock to the extensive margin of labor adjustment - a rise in separations - produces large and persistent negative effects on output, unemployment and welfare, raises precautionary savings and lowers inflation, in line with early evidence about inflation dynamics. Modeling lockdowns as a shock to the intensive margin - a fall in labor utilization - produces small and short-lived macroeconomic and welfare effects, and implies a counterfactual rise in inflation. Conditional on a lockdown (separation) shock, raising public spending or extending UI benefits by large amounts is much more effective in stimulating the economy than during normal times. Quantitatively however, the ability of such policies to flatten the output and unemployment curves remains limited, even though these policies can alleviate a reasonable share of the aggregate welfare losses from the lockdown.
Keywords: Borrowing constraints; Government spending; Incomplete markets; Lockdown; Unemployment; Unemployment insurance.
© 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adjemian, Stéphane, Houtan Bastani, Michel Juillard, Frédéric Karamé, Ferhat Mihoubi, George Perendia, Johannes Pfeifer, Marco Ratto, and Sébastien Villemot. 2011. “Dynare: Reference Manual, Version 4.” Dynare Working Paper 1, CEPREMAP.
-
- Auclert Adrien. Monetary policy and the redistribution channel. Am. Econ. Rev. 2019;109(6):2333–2367.
-
- Auclert, Adrien, Matthew Rognlie, and Ludwig Straub. 2018. “The Intertemporal Keynesian Cross.” NBER Working Paper 25020.
-
- Auray Stéphane, Eyquem Aurélien. Episodes of war and peace in an estimated open economy model. J. Econ. Dyn. Control. 2019;105(C):203–249.
-
- Auray Stéphane, Eyquem Aurélien, Gomme Paul. Ramsey-optimal tax reforms and real exchange rate dynamics. J. Int. Econ. 2018;115:159–169.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

