Electrophoretic Separations on Parafilm-Paper-Based Analytical Devices
- PMID: 32863586
- PMCID: PMC7450514
- DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.06.130
Electrophoretic Separations on Parafilm-Paper-Based Analytical Devices
Abstract
Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (mPADs) have gained significant attention in recent years for applications ranging from clinical diagnostics to environmental testing. However, separation on mPADs remain challenging to implement, particularly in complex samples. This has revived interest in revisiting paper chromatography and paper electrophoresis in mPADs to address these needs. Here, laminated Parafilm-paper (l-paper) is applied to fabricate electrophoretic devices. This approach yields a free-standing channel, leading to improved peak resolution relative to previous electrophoretic separations in traditional wax-printed mPADs. Major factors influencing the separation, including Joule heating, electroosmotic flow, and electrophoretic mobility, were investigated. As a result of paper's high ratio of surface area (78%) to pore volume (22%) resulting in slow heat dissipation, a usable applied field strength range of 0 - 200 V cm-1 was employed to avoid Joule heating. The electroosmotic flow of the system was found to be 2.5 × 10-5 ± 7.7 × 10-7 cm2 V-1s-1 and the electrophoretic mobility of chlorophenol red was 1.2 × 10-4 ± 7.7 × 10-7 cm2 V-1s-1. Basic separation protocols were optimized using colorimetric detection of chlorophenol red and indigo carmine dyes as representative molecules. Paper type, channel width, and applied potential were then used to optimize the separations. Addition of an injection port to the device improved resolution and reduced peak broadening. Finally, the separation of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and L-glutamic acid (Glu) labeled with FITC, was successfully carried out using the l-paper electrophoretic device. Imaging with a microscope was found to achieve reduced peak broadening and increased resolution relative to imaging with a mobile camera, due to elimination of background signal, achieving a 72 ± 4% conjugation of Glu and FITC.
Keywords: Electrophoresis; Electrophoretic laminated Parafilm-paper based analytical devices; Joule heating; L-glutamic acid labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate.
Figures
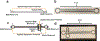


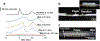


Similar articles
-
Sample injection and electrophoretic separation on a simple laminated paper based analytical device.Electrophoresis. 2016 Feb;37(3):476-81. doi: 10.1002/elps.201500321. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Electrophoresis. 2016. PMID: 26542435
-
Joule Heating-Induced Dispersion in Open Microfluidic Electrophoretic Cytometry.Anal Chem. 2017 Dec 5;89(23):12787-12796. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03096. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Anal Chem. 2017. PMID: 29110464
-
[In-site electrophoretic elution of excessive fluorescein isothiocyanate from fluorescent particles in gel for image analysis].Se Pu. 2022 Jul;40(7):610-615. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.04023. Se Pu. 2022. PMID: 35791599 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Electrophoretic separations on paper: Past, present, and future-A review.Anal Chim Acta. 2017 Sep 8;985:7-23. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.06.015. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Anal Chim Acta. 2017. PMID: 28864197 Review.
-
Column-coupling strategies for multidimensional electrophoretic separation techniques.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015 Jan;407(1):119-38. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-8099-7. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25228075 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Developments in Microfluidic Paper-based Analytical Devices for Pharmaceutical Analysis.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(27):2241-2260. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666221027144310. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36305123
References
-
- Cate DM, Adkins JA, Mettakoonpitak J, Henry CS, Recent Developments in Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices, Analytical Chemistry, 87(2015) 19–41. - PubMed
-
- Mettakoonpitak J, Boehle K, Nantaphol S, Teengam P, Adkins JA, Srisa-Art M, et al., Electrochemistry on Paper-based Analytical Devices: A Review, Electroanalysis, 28(2016) 1420–36.
-
- Almeida MIGS, Jayawardane BM, Kolev SD, McKelvie ID, Developments of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs) for water analysis: A review, Talanta, 177(2018) 176–90. - PubMed
-
- Adkins J, Boehle K, Henry C, Electrochemical paper-based microfluidic devices, ELECTROPHORESIS, 36(2015) 1811–24. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
