Flecainide intoxication in pediatric patients with supraventricular tachycardia
- PMID: 32863668
- PMCID: PMC7437626
- DOI: 10.4103/apc.APC_116_19
Flecainide intoxication in pediatric patients with supraventricular tachycardia
Abstract
Flecainide is a class IC antiarrhythmic indicated for ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias in pediatric patients without structural heart disease. Flecainide has a narrow therapeutic window and proarrhythmic effect even in therapeutic doses and could lead to a life-threatening intoxication. Dosage errors, accidental intakes, and drug or food interactions, especially with dairy products, can be the cause of the intoxication. We report three consecutive cases of flecainide intoxication in children with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) in our hospital from 2017 to 2019. Two cases had complete and spontaneous normalization of electrocardiogram (ECG) after flecainide removal. However, admission to the intensive care was required due to a sustained ventricular tachycardia in one case. Flecainide intoxication can be a life-threatening complication in patients with SVT. We believe all children should have close monitoring with serial ECG and plasma levels of flecainide during the 48-72 h after initiation of treatment, and consider hospitalization for patients <1 year of age.
Keywords: Arrhythmia; children; flecainide; intoxication; supraventricular tachycardia.
Copyright: © 2020 Annals of Pediatric Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
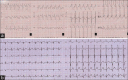
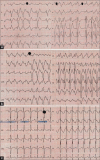
References
-
- Brugada J, Blom N, Sarquella-Brugada G, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Deanfield J, Janousek J, et al. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapy for arrhythmias in the pediatric population: EHRA and AEPC-Arrhythmia Working Group joint consensus statement. Europace. 2013;15:1337–82. - PubMed
-
- Köppel C, Oberdisse U, Heinemeyer G. Clinical course and outcome in class IC antiarrhythmic overdose. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1990;28:433–44. - PubMed
-
- Perry JC, Garson A., Jr Flecainide acetate for treatment of tachyarrhythmias in children: Review of world literature on efficacy, safety, and dosing. Am Heart J. 1992;124:1614–21. - PubMed
-
- Close BR, Banks CJ. Pediatric flecainide toxicity from a double dose. Am J Emerg Med. 2012;30:2095e1–2. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
