Clinical implication of prognostic and predictive biomarkers for castration-resistant prostate cancer: a systematic review
- PMID: 32863768
- PMCID: PMC7448351
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-01508-0
Clinical implication of prognostic and predictive biomarkers for castration-resistant prostate cancer: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Diagnosis of metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) with current biomarkers is difficult and often results in unnecessary invasive procedures as well as over-diagnosis and over-treatment. There are a number of prognostic biomarkers for CRPC, but there are no validated predictive biomarkers to guide in clinical decision-making. Specific biomarkers are needed that enable to understand the natural history and complex biology of this heterogeneous malignancy, identify early response to treatment outcomes and to identify the population of men most likely to benefit from the treatment. In this systematic review, we discuss the existing literature for the role of biomarkers in CRPC and how they aid in the prognosis, treatment selection and survival outcomes.
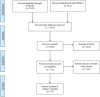
Methods: We performed a literature search on PubMed and EMBASE databases from January 2015 through February 2020 in accordance to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis guidelines. Articles were assessed to identify relevant observational studies and randomized controlled trials regarding biomarkers which aid in identifying progression to mCRPC as well as predictive biomarkers which help in treatment selection.
Results: We identified 3640 number of hits of which 58 articles were found to be relevant. Here we addressed biomarkers in the context of prognosis, prediction and patient selection of therapy. These biomarkers were found to be effective as prognostic or predictive factors under variety of conditions. The higher levels for all these biomarkers were associated with shorter median OS and sometimes PFS. Lower amounts of biomarkers in serum or urine were associated with prolonged survival outcomes, longer time to CRPC development or CRPC progression and longer median follow-up irrespective of any therapy.
Conclusion: We observed that the biomarkers included in our study predicted clinically relevant survival outcomes and treatment exposure. Though the current biomarkers are prognostic when measured prior to initiating treatment, not all are validated as predictive markers in post treatment setting. A greater understanding of biomarkers in CRPC is need of the hour for development of more personalized approach to maximize benefit and minimize harm in men with CRPC.
Keywords: Biomarker; Metastatic cancer; Predictive; Prognostic; Prostate cancer.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Cancer Today. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/. Accessed 24 Apr 2020.
-
- Cornford P, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E, De Santis M, Gross T, et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: treatment of relapsing, metastatic, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2017;71:630–642. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources