Effects of Topical Ozone Application on Outcomes after Accelerated Corneal Collagen Cross-linking: An Experimental Study
- PMID: 32864059
- PMCID: PMC7431725
- DOI: 10.18502/jovr.v15i3.7447
Effects of Topical Ozone Application on Outcomes after Accelerated Corneal Collagen Cross-linking: An Experimental Study
Abstract
Purpose: Ozone is a trioxygen molecule that spontaneously degrades into oxygen and oxygen free radicals. This study was designed to assess the effects of topical ozone application on outcomes after corneal collagen cross-linking (CXL).
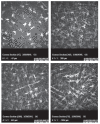
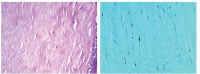
Methods: Enucleated fresh cadaver yearling sheep eyes (n = 28) were divided into five groups: control (C, n = 6), sham (S, n = 6), ozone only (Z, n = 6), CXL only (X, n = 5), and Ozone + CXL (ZX, n = 5). In all groups, except C, the epithelial layer was removed. In group Z, 20 μg/mL liquid ozone was topically applied. In group X, CXL was performed in the accelerated pulse mode. In group ZX, both CXL and ozone were applied. Post-interventional oxygen levels were determined and corneal confocal microscopy and optical coherence tomography were performed. Corneas were evaluated using light and electron microscopy.
Results: Pre-interventional central corneal thickness (CCT) was highest in the control group and considerably similar in the remaining groups (P = 0.006). Pre- and post-interventional CCT were significantly different in the ozonated groups (Z and ZX) (P = 0.028; P = 0.043). Demarcation line depths were similar in groups Z, X, and ZX (P = 0.343). Increased stromal tissue reflectivity was observed in groups Z, X, and ZX. Oxygen levels were higher in the ozonated groups (Z and ZX) (P = 0.006), and caspase activity was higher in the CXL groups (X and ZX) (P = 0.028) as compared to the other groups. Group ZX showed tighter, more regular, and parallel fibrils.
Conclusion: Ozone increases corneal stromal oxygenation which can probably augment the effect of CXL. Future studies should investigate the safety and feasibility of ozone application during CXL.
Keywords: Corneal Collagen Cross-linking; Corneal Confocal Microscopy; Corneal Oxygen; Experimental; Ozone.
Copyright © 2020 Dogan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Gomes JA, Tan D, Rapuano CJ, Belin MW, Ambrósio R Jr, Guell JL, et al. Group of panelists for the Global Delphi Panel of Keratoconus and Ectatic Diseases. Global consensus on keratoconus and ectatic diseases. Cornea 2015;34:359–369. - PubMed
-
- Meek KM, Tuft SJ, Huang YF, Gill PS, Hayes S, Newton RH, Bron AJ. Changes in collagen orientation and distribution in keratoconus corneas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005;46:1948–1956. - PubMed
-
- Wollensak G, Spoerl E, Seiler T. Riboflavin/ultraviolet a-induced collagen crosslinking for the treatment of keratoconus. Am J Ophthalmol 2003;135:620–627. - PubMed
-
- Wollensak G, Wilsch M, Spoerl E, Seiler T. Collagen fiber diameter in the rabbit cornea after collagen crosslinking by riboflavin/UVA. Cornea 2004;23:503–507. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
