Ischemic stroke lesion detection, characterization and classification in CT images with optimal features selection
- PMID: 32864172
- PMCID: PMC7438466
- DOI: 10.1007/s13534-020-00158-5
Ischemic stroke lesion detection, characterization and classification in CT images with optimal features selection
Abstract
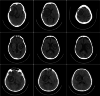
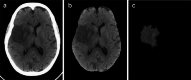
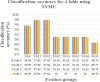
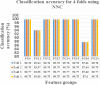
Ischemic stroke is the dominant disorder for mortality and morbidity. For immediate diagnosis and treatment plan of ischemic stroke, computed tomography (CT) images are used. This paper proposes a histogram bin based novel algorithm to segment the ischemic stroke lesion using CT and optimal feature group selection to classify normal and abnormal regions. Steps followed are pre-processing, segmentation, extracting texture features, feature ranking, feature grouping, classification and optimal feature group (FG) selection. The first order features, gray level run length matrix features, gray level co-occurrence matrix features and Hu's moment features are extracted. Classification is done using logistic regression (LR), support vector machine classifier (SVMC), random forest classifier (RFC) and neural network classifier (NNC). This proposed approach effectively detects ischemic stroke lesion with a classification accuracy of 88.77%, 97.86%, 99.79% and 99.79% obtained by the LR, SVMC, RFC and NNC when FG12 is opted, which is validated by fourfold cross validation.
Keywords: CAD; CT images; Classification; Features; Histogram; Ischemic stroke.
© Korean Society of Medical and Biological Engineering 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures




References
-
- Xiao-Ying Y, Li-Qiong W, Jin-Gen L, Ning L, Ying W, Jian-Ping L. Chinese herbal medicine Dengzhan–Shengmai capsule as adjunctive treatment for ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Complement Ther Med. 2017 - PubMed
-
- Paramasivam S. Current trends in the management of acute ischemic stroke. Neurol India. 2015;63:665–672. - PubMed
-
- Karthik R, Menaka R. A critical appraisal on wavelet based features from brain MR images for efficient characterization of ischemic stroke injuries. Electron Lett Comput Vis Image Anal. 2016;15(3):1–16.
-
- Karthik R, Menaka R. Computer-aided detection and characterization of stroke lesion—a short review on the current state-of-the art methods. Imaging Sci J. 2018;66(1):1–22.
-
- Sivakumar P, Ganeshkumar P. An efficient automated methodology for detecting and segmenting the ischemic stroke in brain MRI images. Int J Imaging Syst Technol. 2017;27:265–272.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
