Risk factors and outcome of COVID-19 in patients with hematological malignancies
- PMID: 32864192
- PMCID: PMC7445734
- DOI: 10.1186/s40164-020-00177-z
Risk factors and outcome of COVID-19 in patients with hematological malignancies
Abstract
Background: Prognostic factors of poor outcome in patients with hematological malignancies and COVID-19 are poorly defined.
Patients and methods: This was a Spanish transplant group and cell therapy (GETH) multicenter retrospective observational study, which included a large cohort of blood cancer patients with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection through PCR assays from March 1st 2020 to May 15th 2020.
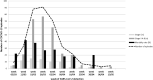
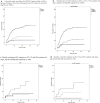
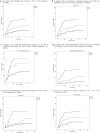
Results: We included 367 pediatric and adult patients with hematological malignancies, including recipients of autologous (ASCT) (n = 58) or allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) (n = 65) from 41 hospitals in Spain. Median age of patients was 64 years (range 1-93.8). Recipients of ASCT and allo-SCT showed lower mortality rates (17% and 18%, respectively) compared to non-SCT patients (31%) (p = 0.02). Prognostic factors identified for day 45 overall mortality (OM) by logistic regression multivariate analysis included age > 70 years [odds ratio (OR) 2.1, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.2-3.8, p = 0.011]; uncontrolled hematological malignancy (OR 2.9, 95% CI 1.6-5.2, p < 0.0001); ECOG 3-4 (OR, 2.56, 95% CI 1.4-4.7, p = 0.003); neutropenia (< 0.5 × 109/L) (OR 2.8, 95% CI 1.3-6.1, p = 0.01); and a C-reactive protein (CRP) > 20 mg/dL (OR 3.3, 95% CI 1.7-6.4, p < 0.0001). In multivariate analysis of 216 patients with very severe COVID-19, treatment with azithromycin or low dose corticosteroids was associated with lower OM (OR 0.42, 95% CI 0.2-0.89 and OR 0.31, 95% CI 0.11-0.87, respectively, p = 0.02) whereas the use of hidroxycloroquine did not show significant improvement in OM (OR 0.64, 95% CI 0.37-1.1, P = 0.1).
Conclusions: In most patients with hematological malignancies COVID-19 mortality was directly driven by older age, disease status, performance status, as well as by immune (neutropenia) parameters and level of inflammation (high CRP). Use of azithromycin and low dose corticosteroids may be of value in very severe COVID-19.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Liu H, Wu Y, Zhang L, Yu Z, Fang M, Yu T, Wang Y, et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang Jing, Zheng Ya, Gou Xi, Ke Pu, Chen Zhaofeng, Guo Qinghong, Ji Rui, Wang Haojia, Wang Yuping, Zhou Yongning. Prevalence of comorbidities in the novel Wuhan coronavirus (COVID-19) infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

