Sequencing, assembly, annotation, and gene expression: novel insights into browning-resistant Luffa cylindrica
- PMID: 32864209
- PMCID: PMC7425639
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.9661
Sequencing, assembly, annotation, and gene expression: novel insights into browning-resistant Luffa cylindrica
Abstract
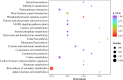
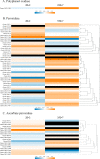
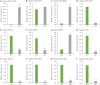
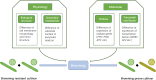
Luffa is a kind of melon crop widely cultivated in temperate regions worldwide. Browning is one of the serious factors affecting the quality of Luffa. Therefore, the molecular mechanism of Luffa browning is of great significance to study. However, the molecular diversity of Luffa cultivars with different browning-resistant abilities has not been well elucidated. In our study, we used high-throughput sequencing to determine the transcriptome of two Luffa cylindrica cultivars '2D-2' and '35D-7'. A total of 115,099 unigenes were clustered, of which 22,607 were differentially expression genes (DEGs). Of these DEGs, 65 encoding polyphenol oxidase, peroxidase, or ascorbate peroxidase were further analyzed. The quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) data indicated that the expression levels of the LcPPO gene (Accession No.: Cluster-21832.13892) was significantly higher in '35D-7' compared with that in '2D-2'. Several POD genes (Accession No.: Cluster-21832.19847, Cluster-21832.30619 and Cluster-48491.2) were also upregulated. Analysis of the plantTFDB database indicated that some transcription factors such as WRKY gene family may also participate in the regulation of Luffa browning. The results indicated that the divergence of genes expression related to enzymatic reaction may lead to the different browning resistances of Luffa. Our study will provide a theoretical basis for breeding of browning-resistant Luffa.
Keywords: Browning; Expression; Luffa; Polyphenol oxidase; Transcriptome.
©2020 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide transcriptome profiling reveals novel insights into Luffa cylindrica browning.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Aug 7;463(4):1243-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.093. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26086104
-
De novo sequencing and analysis of the transcriptome during the browning of fresh-cut Luffa cylindrica 'Fusi-3' fruits.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 16;12(11):e0187117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187117. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29145430 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of Luffa cylindrica (L.) Roem response to infection with Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV).Gene. 2020 May 5;737:144451. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144451. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32035243
-
Identification of browning-related microRNAs and their targets reveals complex miRNA-mediated browning regulatory networks in Luffa cylindrica.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 2;8(1):16242. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33896-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30389964 Free PMC article.
-
Long-read sequencing and de novo assembly of the Luffa cylindrica (L.) Roem. genome.Mol Ecol Resour. 2020 Mar;20(2):511-519. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13129. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Mol Ecol Resour. 2020. PMID: 31869503
Cited by
-
Homologous Cloning of Potassium Channel Genes From the Superior Apple Rootstock Line 12-2, Which is Tolerant to Apple Replant Disease.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 26;13:803160. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.803160. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35154275 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of suitable reference genes for quantitative reverse transcription PCR in Luffa (Luffa cylindrica).Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022 Apr;28(4):737-747. doi: 10.1007/s12298-022-01182-8. Epub 2022 May 3. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022. PMID: 35592479 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the molecular mechanisms of browning tolerance in luffa: a transcriptome and metabolome analysis.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jun 10;16:1530531. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1530531. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40556689 Free PMC article.
-
Study on browning mechanism of fresh-cut eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) based on metabolomics, enzymatic assays and gene expression.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 25;11(1):6937. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86311-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33767263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachem CWB, Speckmann GJ, Vanderlinde PCG, Verheggen FTM, Hunt MD, Stefffens JC, Zabeau M. Antisense expression of polyphenol oxidase genes inhibits enzymatic browning in potato-tubers. Bio-Technology. 1994;12(11):1101–1105. doi: 10.1038/nbt1194-1101. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

