Managing the COVID-19 Pandemic: Research Strategies Based on the Evolutionary and Molecular Characteristics of Coronaviruses
- PMID: 32864575
- PMCID: PMC7445016
- DOI: 10.1007/s42399-020-00457-z
Managing the COVID-19 Pandemic: Research Strategies Based on the Evolutionary and Molecular Characteristics of Coronaviruses
Abstract
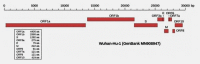
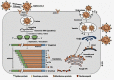
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), an ongoing global health emergency, is a highly transmittable and pathogenic viral infection caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Emerging in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, it spread widely across the world causing panic-worst ever economic depression is visibly predictable. Coronaviruses (CoVs) have emerged as a major public health concern having caused three zoonotic outbreaks; severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV (SARS-CoV) in 2002-2003, Middle East respiratory syndrome-CoV (MERS-CoV) in 2012, and currently this devastating COVID-19. Research strategies focused on understanding the evolutionary origin, transmission, and molecular basis of SARS-CoV-2 and its pathogenesis need to be urgently formulated to manage the current and possible future coronaviral outbreaks. Current response to the COVID-19 outbreak has been largely limited to monitoring/containment. Although frantic global efforts for developing safe and effective prophylactic and therapeutic agents are on, no licensed antiviral treatment or vaccine exists till date. In this review, research strategies for coping with COVID-19 based on evolutionary and molecular aspects of coronaviruses have been proposed.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; MERS-CoV; SARS-CoV; SARS-CoV-2.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Current status of antivirals and druggable targets of SARS CoV-2 and other human pathogenic coronaviruses.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 Dec;53:100721. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100721. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 33132205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: A Global Challenge with Old History, Epidemiology and Progress So Far.Molecules. 2020 Dec 23;26(1):39. doi: 10.3390/molecules26010039. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33374759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: Diagnostics, Therapeutic Advances, and Vaccine Development.Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. 2021;8(3):152-166. doi: 10.1007/s40588-021-00157-9. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33614398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Strategies of Antiviral Drug Discovery for COVID-19.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 13;8:671263. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.671263. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34055887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The outbreak of the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): A review of the current global status.J Infect Public Health. 2020 Nov;13(11):1601-1610. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.011. Epub 2020 Aug 4. J Infect Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32778421 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of clinico-biochemical and inflammatory biomarkers on the immunogenicity and efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 adenoviral vaccine: a longitudinal study.J Circ Biomark. 2023 Sep 20;12:34-43. doi: 10.33393/jcb.2023.2480. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. J Circ Biomark. 2023. PMID: 37744159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradburne AF, Tyrrell DAJ. Coronaviruses of man. Prog Med Virol. 1971;13:373–403.
-
- Woo PC, Lau SK, Lam CS, Lau CC, Tsang AK, Lau JH, et al. Discovery of seven novel mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J Virol. 2012;86:3995–4008. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van der Hoek L. Human coronaviruses: what do they cause? Antivir Ther. 2007;12:651–658. - PubMed
-
- Rose RM, Pinkston P, O'Donnell C, Jensen WA. Viral infection of the lower respiratory tract. Clin Chest Med. 1987;8:405–418. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
