Pain modulation effect on motor cortex after optogenetic stimulation in shPKCγ knockdown dorsal root ganglion-compressed Sprague-Dawley rat model
- PMID: 32865105
- PMCID: PMC7466896
- DOI: 10.1177/1744806920943685
Pain modulation effect on motor cortex after optogenetic stimulation in shPKCγ knockdown dorsal root ganglion-compressed Sprague-Dawley rat model
Abstract
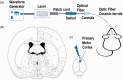
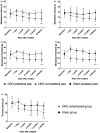
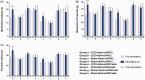
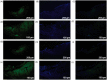
Neuropathic pain can be generated by chronic compression of dorsal root ganglion (CCD). Stimulation of primary motor cortex can disrupt the nociceptive sensory signal at dorsal root ganglion level and reduce pain behaviors. But the mechanism behind it is still implicit. Protein kinase C gamma is known as an essential enzyme for the development of neuropathic pain, and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C gamma can disrupt the sensory signal and reduce pain behaviors. Optogenetic stimulation has been emerged as a new and promising conducive method for refractory neuropathic pain. The aim of this study was to provide evidence whether optical stimulation of primary motor cortex can modulate chronic neuropathic pain in CCD rat model. Animals were randomly divided into CCD group, sham group, and control group. Dorsal root ganglion-compressed neuropathic pain model was established in animals, and knocking down of protein kinase C gamma was also accomplished. Pain behavioral scores were significantly improved in the short hairpin Protein Kinase C gamma knockdown CCD animals during optic stimulation. Ventral posterolateral thalamic firing inhibition was also observed during light stimulation on motor cortex in CCD animal. We assessed alteration of pain behaviors in pre-light off, stimulation-light on, and post-light off state. In vivo extracellular recording of the ventral posterolateral thalamus, viral expression in the primary motor cortex, and protein kinase C gamma expression in dorsal root ganglion were investigated. So, optical cortico-thalamic inhibition by motor cortex stimulation can improve neuropathic pain behaviors in CCD animal, and knocking down of protein kinase C gamma plays a conducive role in the process. This study provides feasibility for in vivo optogenetic stimulation on primary motor cortex of dorsal root ganglion-initiated neuropathic pain.
Keywords: Optogenetics; dorsal root ganglia; motor cortex; neuropathic pain; protein kinase C gamma; thalamus.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CaMKIIα-NpHR-Mediated Optogenetic Inhibition of DRG Glutamatergic Neurons by Flexible Optic Fiber Alleviates Chronic Neuropathic Pain.Neuromolecular Med. 2025 Apr 14;27(1):26. doi: 10.1007/s12017-025-08848-y. Neuromolecular Med. 2025. PMID: 40227491
-
Optical Modulation on the Nucleus Accumbens Core in the Alleviation of Neuropathic Pain in Chronic Dorsal Root Ganglion Compression Rat Model.Neuromodulation. 2020 Feb;23(2):167-176. doi: 10.1111/ner.13059. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Neuromodulation. 2020. PMID: 32103594
-
Optogenetic stimulation of the motor cortex alleviates neuropathic pain in rats of infraorbital nerve injury with/without CGRP knock-down.J Headache Pain. 2020 Aug 26;21(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-01174-7. J Headache Pain. 2020. PMID: 32847499 Free PMC article.
-
Are voltage-gated sodium channels on the dorsal root ganglion involved in the development of neuropathic pain?Mol Pain. 2011 Feb 23;7:16. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-16. Mol Pain. 2011. PMID: 21345196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Narrative Review of Neuropathic Pain: From Pathophysiology to Surgical Treatment.Cureus. 2024 Apr 11;16(4):e58025. doi: 10.7759/cureus.58025. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38738050 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dissecting the Neural Circuitry for Pain Modulation and Chronic Pain: Insights from Optogenetics.Neurosci Bull. 2022 Apr;38(4):440-452. doi: 10.1007/s12264-022-00835-8. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Neurosci Bull. 2022. PMID: 35249185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transplantation of human embryonic stem cells alleviates motor dysfunction in AAV2-Htt171-82Q transfected rat model of Huntington's disease.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Nov 22;12(1):585. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02653-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34809707 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Intrathecal Platelet-Rich Plasma Administration in Alleviation of Chronic Neuropathic Pain in Rat Model.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul 2. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-05173-0. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40601220
-
Transcriptome profiling of microRNAs reveals potential mechanisms of manual therapy alleviating neuropathic pain through microRNA-547-3p-mediated Map4k4/NF-κb signaling pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Sep 1;19(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02568-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 36045396 Free PMC article.
-
CaMKIIα-NpHR-Mediated Optogenetic Inhibition of DRG Glutamatergic Neurons by Flexible Optic Fiber Alleviates Chronic Neuropathic Pain.Neuromolecular Med. 2025 Apr 14;27(1):26. doi: 10.1007/s12017-025-08848-y. Neuromolecular Med. 2025. PMID: 40227491
References
-
- Kim J, Ryu SB, Lee SE, Shin J, Jung HH, Kim SJ, Kim KH, Chang JW. Motor cortex stimulation and neuropathic pain: how does motor cortex stimulation affect pain-signaling pathways? J Neurosurg 2016; 124: 866–876. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Larrea L, Peyron R. Motor cortex stimulation for neuropathic pain: from phenomenology to mechanisms. Neuroimage 2007; 37: S71–S79. - PubMed
-
- Lefaucheur J-P, Drouot X, Cunin P, Bruckert R, Lepetit H, Créange A, Wolkenstein P, Maison P, Keravel Y, Nguyen J-P. Motor cortex stimulation for the treatment of refractory peripheral neuropathic pain. Brain 2009; 132: 1463–1471. - PubMed
-
- Brown JA, Barbaro NM. Motor cortex stimulation for central and neuropathic pain: current status. Pain 2003; 104: 431–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

