Imaging of two samples with a single transmit/receive channel using coupled ceramic resonators for MR microscopy at 17.2 T
- PMID: 32865259
- PMCID: PMC7709743
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.4397
Imaging of two samples with a single transmit/receive channel using coupled ceramic resonators for MR microscopy at 17.2 T
Abstract
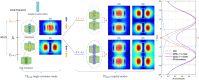
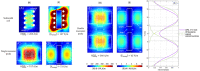
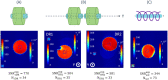
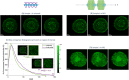
In this paper we address the possibility to perform imaging of two samples within the same acquisition time using coupled ceramic resonators and one transmit/receive channel. We theoretically and experimentally compare the operation of our ceramic dual-resonator probe with a wire-wound solenoid probe, which is the standard probe used in ultrahigh-field magnetic resonance microscopy. We show that due to the low-loss ceramics used to fabricate the resonators, and a favorable distribution of the electric field within the conducting sample, a dual probe, which contains two samples, achieves an SNR enhancement by a factor close to the square root of 2 compared with a solenoid optimized for one sample.
Keywords: dielectric resonators; electromagnetic coupling; magnetic resonance microscopy; signal-to-noise ratio; solenoid.
© 2020 The Authors. NMR in Biomedicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Ciobanu L. Microscopic magnetic resonance imaging: A practical perspective. Singapore: Pan Stanford Publishing; 2017.
-
- Glover P, Mansfield P. Limits to magnetic resonance microscopy. Rep Prog Phys. 2002;65(10):1489‐1511.
-
- Weiger M, Schmidig D, Denoth S, et al. NMR microscopy with isotropic resolution of 3.0 𝜇m using dedicated hardware and optimized methods. Concepts Magn Reson Part B: Magn Reson Eng: Educat J. 2008;33(2):84‐93.
-
- Ciobanu L, Seeber D, Pennington C. 3D MR microscopy with resolution 3.7 𝜇m by 3.3 𝜇m by 3.3 𝜇m. J Magn Reson. 2002;158(1–2):178‐182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

