Role of oxidative stress in epileptogenesis and potential implications for therapy
- PMID: 32865811
- PMCID: PMC7550371
- DOI: 10.1007/s43440-020-00143-w
Role of oxidative stress in epileptogenesis and potential implications for therapy
Abstract
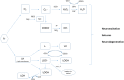
In a state of balance between oxidants and antioxidants, free radicals play an advantageous role of "redox messengers". In a state of oxidative stress, they trigger a cascade of events leading to epileptogenesis. During this latent, free of seizures period, a cascade of neurological changes takes place and finally leads to spontaneous recurrent seizures. The main processes involved in seizure generation are: neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration with anomalous neuroregeneration and lowering seizure threshold. Time of epileptogenesis offers a unique therapeutic window to prevent or at least attenuate seizure development. Animal data indicate that some antioxidants (for instance, resveratrol) may bear an anti-epileptogenic potential.
Keywords: Epileptogenesis; Free radicals; Nitrogen species; Oxidative stress; Oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
Stanislaw J. Czuczwar has received financial support from Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis for lecturing. He is also a recipient of an unrestricted grant from GlaxoSmithKline. Kinga Borowicz-Reutt has no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Beltrán-Sarmiento E, Arregoitia-Sarabia CK, Floriano-Sánchez E, Sandoval-Pacheco R, Galván-Hernández DE, Coballase-Urrutia E, et al. Effects of valproate monotherapy on the oxidant-antioxidant status in Mexican epileptic children: a longitudinal study. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:7954371. doi: 10.1155/2018/7954371. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
