Prevalence of Opioid-Induced Adrenal Insufficiency in Patients Taking Chronic Opioids
- PMID: 32866966
- PMCID: PMC7470471
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa499
Prevalence of Opioid-Induced Adrenal Insufficiency in Patients Taking Chronic Opioids
Abstract
Context: Chronic opioid use may lead to adrenal insufficiency because of central suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. However, the prevalence of opioid-induced adrenal insufficiency (OIAI) is unclear.
Objective: To determine the prevalence of OIAI and to identify predictors for the development of OIAI in patients taking opioids for chronic pain.
Design: Cross-sectional study, 2016-2018.
Setting: Referral center.
Patients: Adult patients taking chronic opioids admitted to the Pain Rehabilitation Center.
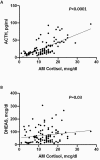
Main outcome measure: Diagnosis of OIAI was considered if positive case detection (cortisol < 10 mcg/dL, ACTH < 15 pg/mL, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate < 25 mcg/dL), and confirmed after endocrine evaluation. Daily morphine milligram equivalent (MME) was calculated.
Results: In 102 patients (median age, 53 years [range, 22-83], 67% women), median daily MME was 60 mg (3-840), and median opioid therapy duration was 60 months (3-360). Abnormal case detection testing was found in 11 (10.8%) patients, and diagnosis of OIAI was made in 9 (9%). Patients with OIAI were on a higher daily MME (median, 140 [20-392] mg vs 57 [3-840] mg, P = 0.1), and demonstrated a 4 times higher cumulative opioid exposure (median of 13,440 vs 3120 mg*months, P = 0.03). No patient taking <MME of 20 mg/day developed OIAI (sensitivity of 100% for MME > 20 mg); however, specificity of MME cutoff >20 mg was only 19%. After opioid discontinuation, 6/7 patients recovered adrenal function.
Conclusion: The prevalence of OIAI was 9%, with MME cumulative exposure being the only predictor for OIAI development. Patients on MME of 20 mg/day and above should be monitored for OIAI.
Keywords: MME; cortisol; diagnosis; morphine; pain; pituitary.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society 2020.
Figures
References
-
- Roehler, DR. Annual surveillance report of drug-related risks and outcomes. https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/pdf/pubs/2019-cdc-drug-surveillance-rep.... 2019. Accessed March 1, 2020 .
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous