Review of Constituents and Biological Activities of Triterpene Saponins from Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma and Its Solubilization Characteristics
- PMID: 32867101
- PMCID: PMC7503449
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25173904
Review of Constituents and Biological Activities of Triterpene Saponins from Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma and Its Solubilization Characteristics
Abstract
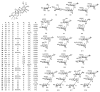
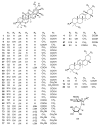
Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma is regarded as one of the most popular and commonly used herbal medicines and has been used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prescriptions for over 2000 years. Pentacyclic triterpene saponins are common secondary metabolites in these plants, which are synthesized via the isoprenoid pathway to produce a hydrophobic triterpenoid aglycone containing a hydrophilic sugar chain. This paper systematically summarizes the chemical structures of triterpene saponins in Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma and reviews and updates their main biological activities studies. Furthermore, the solubilization characteristics, influences, and mechanisms of Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma are elaborated. Solubilization of the triterpene saponins from Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma occurs because they contain the nonpolar sapogenin and water-soluble sidechain. The possible factors affecting the solubilization of Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma are mainly other crude drugs and the pH of the decoction. Triterpene saponins represented by glycyrrhizin from Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma characteristically form micelles due to amphiphilicity, which makes solubilization possible. This overview provides guidance regarding a better understanding of GlycyrrhizaeRadix et Rhizoma and its TCM compatibility, alongside a theoretical basis for the further development and utilization of Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma.
Keywords: Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma; biological activities; glycyrrhizin; solubilization; triterpene saponins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Exploration of differences in decoction phase state, material form, and crystal form between Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma-Gypsum Fibrosum and Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma-CaSO_4·2H_2O based on supramolecules of traditional Chinese medicine].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Jan;50(2):412-421. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240923.301. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 39929622 Chinese.
-
[Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma and discussion of Q-markers].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Jun;46(11):2660-2676. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210304.201. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34296562 Chinese.
-
[Rapid quality evaluation of Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma and Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma Praeparata Cum Melle based on color digitization and multi-component determination].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Dec;47(24):6624-6632. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210401.301. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36604911 Chinese.
-
[Advance in studies on effect of Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma in relieving purgative activity of Rhei Radix et Rhizoma].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015 Feb;40(4):577-81. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26137672 Review. Chinese.
-
Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma: The popular occurrence of herbal medicine applied in classical prescriptions.Phytother Res. 2023 Jul;37(7):3135-3160. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7869. Epub 2023 May 17. Phytother Res. 2023. PMID: 37196671 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on antiviral constituents in traditional Chinese medicines and their mechanisms of action.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1063-1076. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2074053. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35634712 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy, Safety and Economic Evaluation of Wolbigachul-Tang for Chronic Cough Due to Upper Airway Cough Syndrome (UACS): A Study Protocol for Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Comparator Controlled, Parallel, Exploratory Clinical Trial.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Oct 13;11(20):2733. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11202733. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37893807 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of selected terpenoids with two SARS-CoV-2 key therapeutic targets: An in silico study through molecular docking and dynamics simulations.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Jul;134:104538. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104538. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34116362 Free PMC article.
-
Botanical Drugs in Traditional Chinese Medicine With Wound Healing Properties.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 12;13:885484. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.885484. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35645789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New biofunctional effects of oleanane-type triterpene saponins.J Nat Med. 2023 Sep;77(4):644-664. doi: 10.1007/s11418-023-01730-w. Epub 2023 Jul 12. J Nat Med. 2023. PMID: 37436646 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Editorial Committee of Flora of China . Flora of China. Science Press; Beijing, China: 2010.
-
- Li N., Zhou T., Wu F., Wang R., Zhao Q., Zhang J.Q., Yang B.C., Ma B.L. Pharmacokinetic mechanisms underlying the detoxification effect of Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma (Gancao): Drug metabolizing enzymes, transporters, and beyond. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2019;15:167–177. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2019.1563595. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81903816/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2019-JYB-JS-018/the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 2020-JYB-ZDGG-044/the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- BUCM-2019-JCRC002/the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 2020-JYB-YJ-007/the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources