Effectiveness of Protein Supplementation Combined with Resistance Training on Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 32867103
- PMCID: PMC7551830
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12092607
Effectiveness of Protein Supplementation Combined with Resistance Training on Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of the combination of resistance training (RT) and protein supplementation (PS), compared to RT alone or combined with a placebo (plS), in the improvement of muscle strength and physical performance. The search strategy in PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Web of Sciences databases found a total of 294 studies. Once inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied, 16 studies were included for the qualitative analysis. A total of 657 healthy elderly (>60 years) participants were analysed. Finally, 15 articles were included in the quantitative analysis with one being excluded due to issues with data availability. Upper-limb, lower-limb, and handgrip strength were the primary outcomes of the meta-analysis. The secondary outcomes, related to physical performance, were Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), gait speed, and the five-chair-rise test (5CRT). The main results of the meta-analysis show no statistical differences for upper-limb (SMD: 0.56, 95% CI: -0.09, 1.21, p = 0.09, I2 = 68%), lower-limb (SMD: 0.00, 95% CI: -0.18, 0.18, p = 1.0, I2 = 11%), and handgrip strength (SMD: 0.03, 95% CI: -0.26, 0.32, p = 0.84, I2 = 0%) between the RT + PS and the RT alone (or combined with plS). Moreover, no statistical differences were found relating to physical performance. In view of these results, protein supplementation combined with RT does not provide additional benefits compared to RT alone or with plS in healthy elderly adults.
Keywords: elderly; muscle strength; physical performance; protein supplementation; resistance training.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
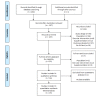
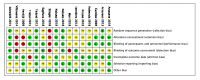
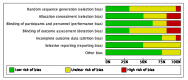
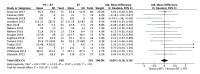

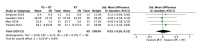
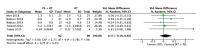
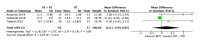
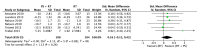
References
-
- García-Hermoso A., Ramirez-Vélez R., Sáez De Asteasu M.L., Martínez-Velilla N., Zambom-Ferraresi F., Valenzuela P.L., Lucia A., Izquierdo M. Safety and Effectiveness of Long-Term Exercise Interventions in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sports Med. 2020;50:1095–1106. doi: 10.1007/s40279-020-01259-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Visser M., Simonsick E.M., Colbert L.H., Brach J., Rubin S.M., Kritchevsky S.B., Newman A.B., Harris T.B. Type and intensity of activity and risk of mobility limitation: The mediating role of muscle parameters. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005;53:762–770. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53257.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

