Follow-Up 18F-FDG PET/CT versus Contrast-Enhanced CT after Ablation of Liver Metastases of Colorectal Carcinoma-A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
- PMID: 32867107
- PMCID: PMC7565889
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12092432
Follow-Up 18F-FDG PET/CT versus Contrast-Enhanced CT after Ablation of Liver Metastases of Colorectal Carcinoma-A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Abstract
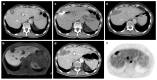
Purpose: After a percutaneous ablation of colorectal liver metastases (CRLM), follow-up investigations to evaluate potential tumor recurrence are necessary. The aim of this study was to analyze whether a combined 18F-Fluordesoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) scan is cost-effective compared to a contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CE-CT) scan for detecting local tumor progression.
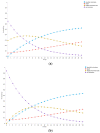
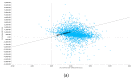
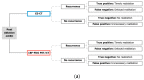
Materials and methods: A decision model based on Markov simulations that estimated lifetime costs and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) was developed. Model input parameters were obtained from the recent literature. Deterministic sensitivity analysis of diagnostic parameters based on a Monte-Carlo simulation with 30,000 iterations was performed. The willingness-to-pay (WTP) was set to $100,000/QALY.
Results: In the base-case scenario, CE-CT resulted in total costs of $28,625.08 and an efficacy of 0.755 QALYs, whereas 18F-FDG PET/CT resulted in total costs of $29,239.97 with an efficacy of 0.767. Therefore, the corresponding incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of 18F-FDG PET/CT was $50,338.96 per QALY indicating cost-effectiveness based on the WTP threshold set above. The results were stable in deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses.
Conclusion: Based on our model, 18F-FDG PET/CT can be considered as a cost-effective imaging alternative for follow-up investigations after percutaneous ablation of colorectal liver metastases.
Keywords: 18F-FDG PET/CT; cost-effectiveness; liver metastases; nuclear imaging; oncologic imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Economic evaluation of 18F-FDG PET/CT, MRI and CE-CT in selection of colorectal liver metastases eligible for ablation - A cost-effectiveness analysis.Eur J Radiol. 2023 Jun;163:110803. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.110803. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Eur J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37004464
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of MRI, CE-CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT for detecting colorectal liver metastases eligible for hepatic resection.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 24;13:1161738. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1161738. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37554160 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of 18F-FDG PET/CT in detecting suspected recurrence or metastasis in well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma patients with negative diagnostic total body scan in Thailand: a decision analysis.J Med Assoc Thai. 2013 Oct;96(10):1350-64. J Med Assoc Thai. 2013. PMID: 24350419
-
Cost-effectiveness of hepatic metastasectomy in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma: a state-transition Monte Carlo decision analysis.Ann Surg. 2003 Apr;237(4):544-55. doi: 10.1097/01.SLA.0000059989.55280.33. Ann Surg. 2003. PMID: 12677152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of distant interval metastases after neoadjuvant therapy for esophageal cancer with 18F-FDG PET(/CT): a systematic review and meta-analysis.Dis Esophagus. 2018 Dec 1;31(12). doi: 10.1093/dote/doy055. Dis Esophagus. 2018. PMID: 29917073
Cited by
-
Identify. Quantify. Predict. Why Immunologists Should Widely Use Molecular Imaging for Coronavirus Disease 2019.Front Immunol. 2021 May 13;12:568959. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.568959. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Local Ablation and Surgery for Liver Metastases of Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 25;13(7):1507. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071507. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33806059 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in PET/CT Imaging for Breast Cancer Patients and Beyond.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 13;12(2):651. doi: 10.3390/jcm12020651. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36675588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zheng J.H., Chang Z.H., Han C.B., Ma J.T., Liu Z.Y., Lu Z.M., Guo Q.Y. Detection of residual tumor following radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases using 18F-FDG PET/PET-CT: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2014;35:339–346. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000057. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

