Proteomics Reveals the Potential Protective Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide on Retinal Ganglion Cells in an Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Animal Model
- PMID: 32867129
- PMCID: PMC7557839
- DOI: 10.3390/ph13090213
Proteomics Reveals the Potential Protective Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide on Retinal Ganglion Cells in an Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Animal Model
Abstract
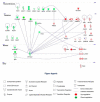
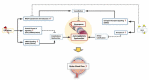
Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness and is characterized by progressive retinal ganglion cell (RGC) degeneration. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a potent neurotransmitter and has been proven to protect RGCs against glaucomatous injury in vitro and in vivo. This study is to provide an overall insight of H2S's role in glaucoma pathophysiology. Ischemia-reperfusion injury (I/R) was induced in Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 12) by elevating intraocular pressure to 55 mmHg for 60 min. Six of the animals received intravitreal injection of H2S precursor prior to the procedure and the retina was harvested 24 h later. Contralateral eyes were assigned as control. RGCs were quantified and compared within the groups. Retinal proteins were analyzed via label-free mass spectrometry based quantitative proteomics approach. The pathways of the differentially expressed proteins were identified by ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA). H2S significantly improved RGC survival against I/R in vivo (p < 0.001). In total 1115 proteins were identified, 18 key proteins were significantly differentially expressed due to I/R and restored by H2S. Another 11 proteins were differentially expressed following H2S. IPA revealed a significant H2S-mediated activation of pathways related to mitochondrial function, iron homeostasis and vasodilation. This study provides first evidence of the complex role that H2S plays in protecting RGC against I/R.
Keywords: glaucoma; hydrogen sulfide; label-free mass spectrometry; mitochondrial function; neuronal apoptosis; signalling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Protects Retinal Ganglion Cells Against Glaucomatous Injury In Vitro and In Vivo.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Oct 1;58(12):5129-5141. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22200. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28986598
-
Relevant variations and neuroprotecive effect of hydrogen sulfide in a rat glaucoma model.Neuroscience. 2017 Jan 26;341:27-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.11.019. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 27890826
-
Hydrogen sulfide supplement attenuates the apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells in experimental glaucoma.Exp Eye Res. 2018 Mar;168:33-48. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2018.01.004. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Exp Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29326065
-
Unmet needs in glaucoma therapy: The potential role of hydrogen sulfide and its delivery strategies.J Control Release. 2022 Jul;347:256-269. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.001. Epub 2022 May 13. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35526614 Review.
-
Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Retinal Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Aug 29;8:588. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00588. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28900398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative proteomic analysis of regenerative mechanisms in mouse retina to identify markers for neuro-regeneration in glaucoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 4;14(1):23118. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72378-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39366989 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide: Novel Endogenous and Exogenous Modulator of Oxidative Stress in Retinal Degeneration Diseases.Molecules. 2021 Apr 21;26(9):2411. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092411. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33919146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide in health and disease.MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 16;5(9):e661. doi: 10.1002/mco2.661. eCollection 2024 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39156767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometry-based retina proteomics.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023 May;42(3):1032-1062. doi: 10.1002/mas.21786. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023. PMID: 35670041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Perspective of Hydrogen Sulfide as a Novel Gaseous Modulator of Oxidative Stress in Glaucoma.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Apr 26;10(5):671. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050671. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33925849 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Flaxman S.R., Bourne R.R.A., Resnikoff S., Ackland P., Braithwaite T., Cicinelli M.V., Das A., Jonas J.B., Keeffe J., Kempen J.H., et al. Global causes of blindness and distance vision impairment 1990–2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health. 2017;5:e1221–e1234. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30393-5. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

