Copper-Polyurethane Composite Materials: Particle Size Effect on the Physical-Chemical and Antibacterial Properties
- PMID: 32867134
- PMCID: PMC7563828
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12091934
Copper-Polyurethane Composite Materials: Particle Size Effect on the Physical-Chemical and Antibacterial Properties
Abstract
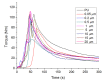
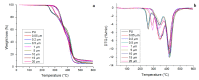
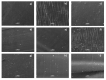
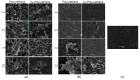
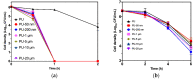
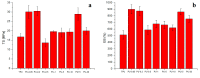
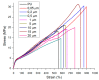
In this work, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) composites incorporated with 1.0 wt% Cu particles were synthesized by the melt blending method. The effect of the incorporated copper particle size on the antibacterial, thermal, rheological, and mechanical properties of TPU was investigated. The obtained results showed that (i) the addition of copper particles increased the thermal and mechanical properties because they acted as co-stabilizers of polyurethane (PU) (ii) copper nanoparticles decreased the viscosity of composite melts, and (iii) microparticles > 0.5 µm had a tendency to easily increase the maximum torque and formation of agglomerates. SEM micrographics showed that a good mixture between TPU and copper particles was obtained by the extrusion process. Additionally, copper-TPU composite materials effectively inhibited the growth of the Gram-negative Escherichia coli and the Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus. Considering that the natural concentration of copper in the blood is in the range of 0.7-0.12 mg/L and that the total migration value of copper particles from TPU was 1000 times lower, the results suggested that TPU nanocomposites could be adequately employed for biomedical applications without a risk of contamination.
Keywords: antibacterial; composite; copper particle; particle size; polyurethane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nano-silver-incorporated biomimetic polydopamine coating on a thermoplastic polyurethane porous nanocomposite as an efficient antibacterial wound dressing.J Nanobiotechnology. 2018 Nov 12;16(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0416-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018. PMID: 30419925 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Activities of Thermoplastic Polyurethane/Clay Nanocomposites against Pathogenic Bacteria.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020 Oct 19;3(10):6672-6679. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c00452. Epub 2020 Oct 1. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020. PMID: 35019393
-
Novel multifunctional nanofibers based on thermoplastic polyurethane and ionic liquid: towards antibacterial, anti-electrostatic and hydrophilic nonwovens by electrospinning.Nanotechnology. 2015 Mar 13;26(10):105704. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/26/10/105704. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Nanotechnology. 2015. PMID: 25686531
-
Investigating Physio-Thermo-Mechanical Properties of Polyurethane and Thermoplastics Nanocomposite in Various Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Jul 27;13(15):2467. doi: 10.3390/polym13152467. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34372071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional Composite Materials Based on Anion Exchangers Modified with Copper Compounds-A Review of Their Synthesis Methods, Characteristics and Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Aug 30;15(17):3606. doi: 10.3390/polym15173606. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37688232 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sustained Release of Linezolid from Prepared Hydrogels with Polyvinyl Alcohol and Aliphatic Dicarboxylic Acids of Variable Chain Lengths.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Oct 17;12(10):982. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12100982. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33080791 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the Antibacterial Performance of Polymer-Based Nanocomposites Induced by Additive Manufacturing Processing.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jan 11;17(2):171. doi: 10.3390/polym17020171. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861243 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Metal-Based Antimicrobial Coatings for High-Touch Surfaces.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 21;23(3):1162. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031162. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tailoring Mesoporous Silica-Coated Silver Nanoparticles and Polyurethane-Doped Films for Enhanced Antimicrobial Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Mar 2;14(5):462. doi: 10.3390/nano14050462. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38470791 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the preparation of antimicrobial material based on thermoplastic polyurethane and drug release control.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jul;15(7):2534-2546. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01751-2. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39623244
References
-
- Nasrollahzadeh M., Sajadi M., Atarod M., Sajjadi M., Issaabadi Z. Interface Science and Technology. 1st ed. Volume 28. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. An Introduction to Green Nanotechnology; pp. 231–316.
-
- Guzmán M.G., Dille J., Godet S. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction method and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Chem. Biol. Eng. 2009;3:104–111.
-
- Becerra A., Rodríguez-Llamazares S., Carrasco C., Díaz-Visurraga J., Riffo C., Mondaca M.A. Preparation of poly(vinyl chloride)/copper nanocomposite films with reduced bacterial adhesion. High Perform. Polym. 2012;25:51–60. doi: 10.1177/0954008312454899. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

