Influence of the Molecular Weight and the Presence of Calcium Ions on the Molecular Interaction of Hyaluronan and DPPC
- PMID: 32867196
- PMCID: PMC7504306
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25173907
Influence of the Molecular Weight and the Presence of Calcium Ions on the Molecular Interaction of Hyaluronan and DPPC
Abstract
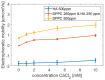
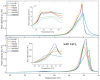
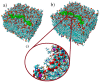
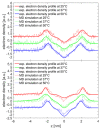
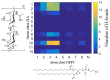
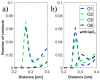
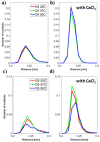
Hyaluronan is an essential physiological bio macromolecule with different functions. One prominent area is the synovial fluid which exhibits remarkable lubrication properties. However, the synovial fluid is a multi-component system where different macromolecules interact in a synergetic fashion. Within this study we focus on the interaction of hyaluronan and phospholipids, which are thought to play a key role for lubrication. We investigate how the interactions and the association structures formed by hyaluronan (HA) and 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC) are influenced by the molecular weight of the bio polymer and the ionic composition of the solution. We combine techniques allowing us to investigate the phase behavior of lipids (differential scanning calorimetry, zeta potential and electrophoretic mobility) with structural investigation (dynamic light scattering, small angle scattering) and theoretical simulations (molecular dynamics). The interaction of hyaluronan and phospholipids depends on the molecular weight, where hyaluronan with lower molecular weight has the strongest interaction. Furthermore, the interaction is increased by the presence of calcium ions. Our simulations show that calcium ions are located close to the carboxylate groups of HA and, by this, reduce the number of formed hydrogen bonds between HA and DPPC. The observed change in the DPPC phase behavior can be attributed to a local charge inversion by calcium ions binding to the carboxylate groups as the binding distribution of hyaluronan and 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine is not changed.
Keywords: binding distribution; hyaluronan; molecular interaction; phase behavior; phospholipid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Structure of DPPC-hyaluronan interfacial layers - effects of molecular weight and ion composition.Soft Matter. 2016 Jan 21;12(3):729-40. doi: 10.1039/c5sm01708d. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Soft Matter. 2016. PMID: 26508354
-
Lubrication synergy: Mixture of hyaluronan and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) vesicles.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 Feb 15;488:225-233. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.10.091. Epub 2016 Nov 1. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 27835815
-
Hyaluronan and phospholipid association in biolubrication.Biomacromolecules. 2013 Dec 9;14(12):4198-206. doi: 10.1021/bm400947v. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Biomacromolecules. 2013. PMID: 24171653
-
The influence of hyaluronan on the structure of a DPPC-bilayer under high pressures.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016 Jun 1;142:230-238. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.02.040. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016. PMID: 26954090
-
Biolubrication synergy: Hyaluronan - Phospholipid interactions at interfaces.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2019 Dec;274:102050. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2019.102050. Epub 2019 Oct 20. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2019. PMID: 31669714 Review.
Cited by
-
Modifying Membranotropic Action of Antimicrobial Peptide Gramicidin S by Star-like Polyacrylamide and Lipid Composition of Nanocontainers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 9;25(16):8691. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168691. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201384 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic acid-lipid binding.BMC Chem. 2021 May 27;15(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s13065-021-00763-0. BMC Chem. 2021. PMID: 34044855 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Synovial Fluid Components: Albumin-Chondroitin Sulfate Interactions Seen through Molecular Dynamics.Materials (Basel). 2022 Oct 6;15(19):6935. doi: 10.3390/ma15196935. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36234275 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic-Resolution Experimental Structural Biology and Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Hyaluronan and Its Complexes.Molecules. 2022 Oct 26;27(21):7276. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217276. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364098 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buhler E., Boue F. Chain persistence length and structure in hyaluronan solutions: Ionic strength dependence for a model semirigid polyelectrolyte. Macromolecules. 2004;37:1600–1610. doi: 10.1021/ma0215520. - DOI
-
- Klein J. Hydration lubrication. Friction. 2013;1:1–23. doi: 10.1007/s40544-013-0001-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

