Characterization of the Heavy-Metal-Associated Isoprenylated Plant Protein (HIPP) Gene Family from Triticeae Species
- PMID: 32867204
- PMCID: PMC7504674
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21176191
Characterization of the Heavy-Metal-Associated Isoprenylated Plant Protein (HIPP) Gene Family from Triticeae Species
Abstract
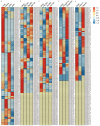
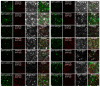
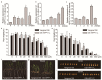
Heavy-metal-associated (HMA) isoprenylated plant proteins (HIPPs) only exist in vascular plants. They play important roles in responses to biotic/abiotic stresses, heavy-metal homeostasis, and detoxification. However, research on the distribution, diversification, and function of HIPPs in Triticeae species is limited. In this study, a total of 278 HIPPs were identified from a database from five Triticeae species, and 13 were cloned from Haynaldia villosa. These genes were classified into five groups by phylogenetic analysis. Most HIPPs had one HMA domain, while 51 from Clade I had two, and all HIPPs had good collinear relationships between species or subgenomes. In silico expression profiling revealed that 44 of the 114 wheat HIPPs were dominantly expressed in roots, 43 were upregulated under biotic stresses, and 29 were upregulated upon drought or heat treatment. Subcellular localization analysis of the cloned HIPPs from H. villosa showed that they were expressed on the plasma membrane. HIPP1-V was upregulated in H. villosa after Cd treatment, and transgenic wheat plants overexpressing HIPP1-V showed enhanced Cd tolerance, as shown by the recovery of seed-germination and root-growth inhibition by supplementary Cd. This research provides a genome-wide overview of the Triticeae HIPP genes and proved that HIPP1-V positively regulates Cd tolerance in common wheat.
Keywords: Cd tolerance; HIPP; Haynaldia villosa L.; gene family; subcellular localization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Fang W., Wu P. Elevated selenium and other mineral element concentrations in soil and plant tissue in bone coal sites in Haoping area, Ziyang County, China. Plant Soil. 2004;261:135–146. doi: 10.1023/B:PLSO.0000035580.32406.e3. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2016YFD0101004/National Key Research and Development Program
- 2016YFD0102001-004/National Key Research and Development Program
- 91935304/National Natural Science Foundation of China (Major Program)
- 31661143005/International Cooperation and Exchange of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31971943/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2015-Z41/'948' Project of Ministry of Agriculture
- BA2017138/Jiangsu Province for the transformation of scientific and technological achievements
- B08025/Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities
- PZCZ201706/Creation of Major New Agricultural Varieties in Jiangsu Province
- JATS [2019] 429/Jiangsu Agricultural Technology System (JATS)
- 2019BBF02022-04/Key Research and Development Major Project of Ningxia Autonomous Region
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

