Probiotics: Versatile Bioactive Components in Promoting Human Health
- PMID: 32867260
- PMCID: PMC7560221
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina56090433
Probiotics: Versatile Bioactive Components in Promoting Human Health
Abstract
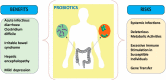
The positive impact of probiotic strains on human health has become more evident than ever before. Often delivered through food, dietary products, supplements, and drugs, different legislations for safety and efficacy issues have been prepared. Furthermore, regulatory agencies have addressed various approaches toward these products, whether they authorize claims mentioning a disease's diagnosis, prevention, or treatment. Due to the diversity of bacteria and yeast strains, strict approaches have been designed to assess for side effects and post-market surveillance. One of the most essential delivery systems of probiotics is within food, due to the great beneficial health effects of this system compared to pharmaceutical products and also due to the increasing importance of food and nutrition. Modern lifestyle or various diseases lead to an imbalance of the intestinal flora. Nonetheless, as the amount of probiotic use needs accurate calculations, different factors should also be taken into consideration. One of the novelties of this review is the presentation of the beneficial effects of the administration of probiotics as a potential adjuvant therapy in COVID-19. Thus, this paper provides an integrative overview of different aspects of probiotics, from human health care applications to safety, quality, and control.
Keywords: clinical studies; evidence based-medicine; lifestyle; mechanisms; nutrition; probiotic properties; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Salehi B., Lopez-Jornet P., Pons-Fuster López E., Calina D., Sharifi-Rad M., Ramírez-Alarcón K., Forman K., Fernández M., Martorell M., Setzer W.N. Plant-derived bioactives in oral mucosal lesions: A key emphasis to curcumin, lycopene, chamomile, aloe vera, green tea and coffee properties. Biomolecules. 2019;9:106. doi: 10.3390/biom9030106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sharifi-Rad M., Kumar N.V.A., Zucca P., Varoni E.M., Dini L., Panzarini E., Rajkovic J., Tsouh Fokou P.V., Azzini E., Peluso I., et al. Lifestyle, oxidative stress and antioxidants: Back and forth in the pathophysiology of chronic diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020;11:694. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00694. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

