Synthesis, In Silico and In Vitro Evaluation for Acetylcholinesterase and BACE-1 Inhibitory Activity of Some N-Substituted-4-Phenothiazine-Chalcones
- PMID: 32867308
- PMCID: PMC7504348
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25173916
Synthesis, In Silico and In Vitro Evaluation for Acetylcholinesterase and BACE-1 Inhibitory Activity of Some N-Substituted-4-Phenothiazine-Chalcones
Abstract
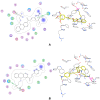
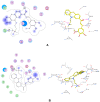
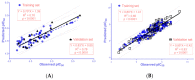
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and beta-secretase (BACE-1) are two attractive targets in the discovery of novel substances that could control multiple aspects of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Chalcones are the flavonoid derivatives with diverse bioactivities, including AChE and BACE-1 inhibition. In this study, a series of N-substituted-4-phenothiazine-chalcones was synthesized and tested for AChE and BACE-1 inhibitory activities. In silico models, including two-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (2D-QSAR) for AChE and BACE-1 inhibitors, and molecular docking investigation, were developed to elucidate the experimental process. The results indicated that 13 chalcone derivatives were synthesized with relatively high yields (39-81%). The bioactivities of these substances were examined with pIC50 3.73-5.96 (AChE) and 5.20-6.81 (BACE-1). Eleven of synthesized chalcones had completely new structures. Two substances AC4 and AC12 exhibited the highest biological activities on both AChE and BACE-1. These substances could be employed for further researches. In addition to this, the present study results suggested that, by using a combination of two types of predictive models, 2D-QSAR and molecular docking, it was possible to estimate the biological activities of the prepared compounds with relatively high accuracy.
Keywords: BACE-1; QSAR; acetylcholiesterase inhibitor; chalcone; docking; in silico.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural Modifications on Chalcone Framework for Developing New Class of Cholinesterase Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 14;23(6):3121. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063121. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, In Silico and In Vitro Evaluation of Some Flavone Derivatives for Acetylcholinesterase and BACE-1 Inhibitory Activity.Molecules. 2020 Sep 5;25(18):4064. doi: 10.3390/molecules25184064. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32899576 Free PMC article.
-
Design of Curcumin and Flavonoid Derivatives with Acetylcholinesterase and Beta-Secretase Inhibitory Activities Using in Silico Approaches.Molecules. 2020 Aug 10;25(16):3644. doi: 10.3390/molecules25163644. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32785161 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of the 4-Substituted 2-Hydroxy-5-Iodochalcones and Their 7-Substituted 6-Iodoflavonol Derivatives for Inhibitory Effect on Cholinesterases and β-Secretase.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 18;19(12):4112. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124112. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30567381 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Properties of Chalcones: A Review of Preclinical Including Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Evidence.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 18;11:592654. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.592654. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33536909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Flavonoid and Chalcone Scaffolds as Inhibitors of BACE1: Recent Updates.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(9):1243-1256. doi: 10.2174/1386207326666230731092409. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37519205 Review.
-
Structural Modifications on Chalcone Framework for Developing New Class of Cholinesterase Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 14;23(6):3121. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063121. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Developments in New Therapeutic Agents against Alzheimer and Parkinson Diseases: In-Silico Approaches.Molecules. 2021 Apr 11;26(8):2193. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082193. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33920326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of Ramalin and Its Derivatives for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2021 Oct 26;26(21):6445. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216445. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770857 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Mechanism of Linearized-Microcystinase Involved in Bacterial Degradation of Microcystins.Front Microbiol. 2021 Mar 30;12:646084. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.646084. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33859631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association 2015 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2015;11:332–384. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

