PPARGC1A rs8192678 and NRF1 rs6949152 Polymorphisms Are Associated with Muscle Fiber Composition in Women
- PMID: 32867330
- PMCID: PMC7563119
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11091012
PPARGC1A rs8192678 and NRF1 rs6949152 Polymorphisms Are Associated with Muscle Fiber Composition in Women
Abstract
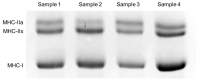
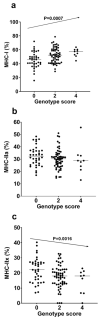
PPARGC1A rs8192678 G/A (Gly482Ser) and NRF1 rs6949152 A/G polymorphisms have been associated with endurance athlete status, endurance performance phenotypes, and certain health-related markers of different pathologies such as metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. We hypothesized that they could be considered interesting candidates for explaining inter-individual variations in muscle fiber composition in humans. We aimed to examine possible associations of these polymorphisms with myosin heavy-chain (MHC) isoforms as markers of muscle fiber compositions in vastus lateralis muscle in a population of 214 healthy Japanese subjects, aged between 19 and 79 years. No significant associations were found in men for any measured variables. In contrast, in women, the PPARGC1A rs8192678 A/A genotype was significantly associated with a higher proportion of MHC-I (p = 0.042) and with a lower proportion of MHC-IIx (p = 0.033), and the NRF1 rs6949152 AA genotype was significantly associated with a higher proportion of MHC-I (p = 0.008) and with a lower proportion of MHC IIx (p = 0.035). In women, the genotype scores of the modes presenting the most significant results for PPARGC1A rs8192678 G/A (Gly482Ser) and NRF1 rs6949152 A/G polymorphisms were significantly associated with MHC-I (p = 0.0007) and MHC IIx (p = 0.0016). That is, women with combined PPARGC1A A/A and NRF1 A/A genotypes presented the highest proportion of MHC-I and the lowest proportion of MHC-IIx, in contrast to women with combined PPARGC1A GG+GA and NRF1 AG+GG genotypes, who presented the lowest proportion of MHC-I and the highest proportion of MHC-IIx. Our results suggest possible associations between these polymorphisms (both individually and in combination) and the inter-individual variability observed in muscle fiber composition in women, but not in men.
Keywords: PGC-1α; SNP; genotype score; myosin heavy chain; nuclear respiratory factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kumagai H., Tobina T., Ichinoseki-Sekine N., Kakigi R., Tsuzuki T., Zempo H., Shiose K., Yoshimura E., Kumahara H., Ayabe M., et al. Role of selected polymorphisms in determining muscle fiber composition in Japanese men and women. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018;124:1377–1384. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00953.2017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kriketos A.D., Pan D.A., Lillioja S., Cooney G.J., Baur L.A., Milner M.R., Sutton J.R., Jenkins A.B., Bogardus C., Storlien L.H. Interrelationships between muscle morphology, insulin action, and adiposity. Am. J. Physiol. 1996;270 Pt 2:R1332–R1339. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1996.270.6.R1332. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

