Antitumor Activity and Mechanism of Robustic Acid from Dalbergia benthami Prain via Computational Target Fishing
- PMID: 32867345
- PMCID: PMC7503938
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25173919
Antitumor Activity and Mechanism of Robustic Acid from Dalbergia benthami Prain via Computational Target Fishing
Abstract
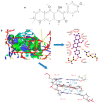
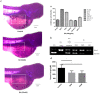
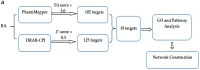
Dalbergia benthami Prain (D.benthami) is an important legume species of the Dalbergia family, due to the use of its trunk and root heart in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). In the present study, we reported the isolation, characterization and pharmacological activities of robustic acid (RA) from the ethyl acetate extract of D. benthami Prain. The SwissADME prediction showed that the RA satisfied the Lipinski's rule of five (molecule weight (MW): 380.39 g/mol, lipid-water partition coefficient (log P): 3.72, hydrogen bond donors (Hdon): 1, hydrogen bond acceptors (Hacc): 6, rotatable bonds (Rbon): 3. Other chemical and pharmacological properties of this RA were also evaluated, including topological polar surface area (TPSA) = 78.13 Å and solubility (Log S) = -4.8. The probability values of the antineoplastic, anti-free radical activities and topoisomerase I (TopoⅠ) inhibitory activity were found to be 0.784, 0.644 and 0.379, respectively. The molecular docking experiment using the Surflex-Dock showed that the Total Score and C Score of RNA binding with the human DNA-Topo I complex were 7.80 and 4. The MTS assay experiment showed that the inhibitory rates of RA on HL-60, MT4, Hela, HepG2, SK-OV-3 and MCF-7 cells were 37.37%, 97.41%, 81.22%, 34.4%, 32.68% and 51.4%, respectively. In addition, RA exhibited an inhibitory effect on the angiogenesis of zebrafish embryo, a good TopoⅠ inhibitory activity at a 10 mM concentration and in a dose-dependent manner, excellent radical scavenging in the DPPH and ABTS assays, and the free radical scavenging rate was close to the positive control (BHT) at different concentrations (0.5-2.0 mg/mL). Furthermore, 18 potential targets were found for this RA by PharmMapper, including ANXA3, SRC, FGFR2, GSK3B, CSNK2B, YARS, LCK, EPHA2, MAPK14, RORA, CRABP2, PPP1CC, METAP2, MME, TTR, MET and KDR. The GO and KEGG pathway analysis revealed that the "protein tyrosine kinase activity", "rap1 signaling pathway" and "PI3K-Akt signaling pathway" were significantly enriched by the RA target genes. Our results will provide new insights into the pharmaceutical use of this species. More importantly, our data will expand our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of RA functions.
Keywords: Dalbergia benthami prain; anti-tumor activity; computational target fishing; robustic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest in association with this manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of New 4-Acyloxy Derivatives of Robustic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 26;20(21):5336. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215336. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31717797 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Design, Synthesis and Docking Study of Alkyl and Benzyl Derivatives of Robustic Acid as Topoisomerase I Inhibitors.Chem Biodivers. 2020 Mar;17(3):e1900556. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201900556. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Chem Biodivers. 2020. PMID: 31943759
-
Chemical composition and evaluation of antioxidant activities, antimicrobial, and anti-melanogenesis effect of the essential oils extracted from Dalbergia pinnata (Lour.) Prain.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 May 23;254:112731. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112731. Epub 2020 Mar 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32135240
-
Bioactive constituents from the stems of Dalbergia parviflora.Fitoterapia. 2009 Oct;80(7):427-31. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2009.06.002. Epub 2009 Jun 11. Fitoterapia. 2009. PMID: 19524648
-
[Neoflavonoids and their pharmacological activities in Dalbergia genus].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Dec;42(24):4707-4715. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170928.013. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29493135 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic insights into the anti-depressant effect of emodin: an integrated systems pharmacology study and experimental validation.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 29;13(11):15078-15099. doi: 10.18632/aging.203072. Epub 2021 May 29. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34051074 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology analysis reveals neuroprotective effects of the Qin-Zhi-Zhu-Dan Formula in Alzheimer's disease.Front Neurosci. 2022 Oct 20;16:943400. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.943400. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36340795 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into the anti-depressant effect of curcumin based on network pharmacology and experimental validation.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jan;397(1):583-598. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02628-w. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37490124
-
The Main Alkaloids in Uncaria rhynchophylla and Their Anti-Alzheimer's Disease Mechanism Determined by a Network Pharmacology Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 31;22(7):3612. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073612. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33807157 Free PMC article.
-
Progranulin as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Immune-Mediated Diseases.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Dec 4;14:6543-6556. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S339254. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34898994 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Editorial Committee of the National Chinese Medicine Administrative Bureau . Chinese Materia Medica. 4th ed. Shanghai Scientific and Technical Education Publishing House; Shanghai, China: 2005. pp. 432–433.
-
- Liu R.-H., Lin S., Zhang P.-Z., Chen L.-Y., Huang H.-L., Mei D.-Y. Neoflavonoids and their pharmacological activities in Dalbergia genus. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2017;42:4707–4715. - PubMed
-
- Chen S.S., Shi X.H. Antibacterial and Anti-inflammatory Effect of Crude Extract of Two Dalbergia Plants. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae. 2018;24:157–162.
-
- Huo L.N., Liu H.G. Evaluation of the antioxidant and alpha-Glucosidase inhibitory activities of different extracts of Dalbergia benthami. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2014;42:242–244.
-
- Wei J.H., Tan H.S. Chemical constituents from Zhuang medicine Dalbergia benthami. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2017;49:2159–2163.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2017KY1368/Promotion project of basic ability of young and middle-aged teachers in colleges and universities in Guangxi
- 2017GXNSFAA198171/Guangxi Natural Science Foundation
- CMEMR2015-B04 and CMEMR2015-B05/State Key Laboratory Cultivation Base for the Chemistry and Molecular Engineeringof Medicinal Resources, Ministry of Science and Technology of China
- NSFC81603525 and 2018KY0861/The National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

