Neuroprotective Properties of Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) in Parkinson's Disease: A Review
- PMID: 32867388
- PMCID: PMC7504552
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25173926
Neuroprotective Properties of Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) in Parkinson's Disease: A Review
Abstract
Neurodegenerative disease is a collective term given for the clinical condition, which results in progressive degeneration of neurons and the loss of functions associated with the affected brain region. Apart from the increase in age, neurodegenerative diseases are also partly affected by diet and lifestyle practices. Parkinson's disease (PD) is a slow onset neurodegenerative disorder and the second most common neurodegenerative disease, which affects the motor system. Although there is no prescribed treatment method to prevent and cure PD, clinical procedures help manage the disease symptoms. Green tea polyphenols are known for several health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective activity. The current manuscript summarizes the possible mechanisms of neuroprotective potential of green tea with a special focus on PD. Studies have suggested that the consumption of green tea protects against free-radicals, inflammation, and neuro-damages. Several in vivo studies aid in understanding the overall mechanism of green tea. However, the same dose may not be sufficient in humans to elicit similar effects due to complex physiological, social, and cultural development. Future research focused on more clinical trials could identify an optimum dose that could impart maximum health benefits to impart neuroprotection in PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; green tea; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroprotection; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
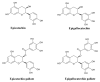
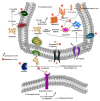
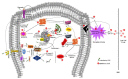
References
-
- Chu D.C. Green Tea—Its cultivation, processing of the leaves for drinking materials and kinds of green tea. In: Yamamoto T., Juneja L.R., Chu D.C., Kim M., editors. Chemistry and Applications of Green Tea. CRC Press; New York, NY, USA: 1997. pp. 1–11.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

