Predicting the most deleterious missense nsSNPs of the protein isoforms of the human HLA-G gene and in silico evaluation of their structural and functional consequences
- PMID: 32867672
- PMCID: PMC7457528
- DOI: 10.1186/s12863-020-00890-y
Predicting the most deleterious missense nsSNPs of the protein isoforms of the human HLA-G gene and in silico evaluation of their structural and functional consequences
Abstract
Background: The Human Leukocyte Antigen G (HLA-G) protein is an immune tolerogenic molecule with 7 isoforms. The change of expression level and some polymorphisms of the HLA-G gene are involved in various pathologies. Therefore, this study aimed to predict the most deleterious missense non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (nsSNPs) in HLA-G isoforms via in silico analyses and to examine structural and functional effects of the predicted nsSNPs on HLA-G isoforms.
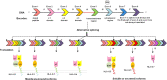
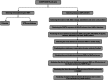
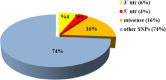
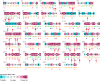
Results: Out of 301 reported SNPs in dbSNP, 35 missense SNPs in isoform 1, 35 missense SNPs in isoform 5, 8 missense SNPs in all membrane-bound HLA-G isoforms and 8 missense SNPs in all soluble HLA-G isoforms were predicted as deleterious by all eight servers (SIFT, PROVEAN, PolyPhen-2, I-Mutant 3.0, SNPs&GO, PhD-SNP, SNAP2, and MUpro). The Structural and functional effects of the predicted nsSNPs on HLA-G isoforms were determined by MutPred2 and HOPE servers, respectively. Consurf analyses showed that the majority of the predicted nsSNPs occur in conserved sites. I-TASSER and Chimera were used for modeling of the predicted nsSNPs. rs182801644 and rs771111444 were related to creating functional patterns in 5'UTR. 5 SNPs in 3'UTR of the HLA-G gene were predicted to affect the miRNA target sites. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed the HLA-G deregulation can serve as a prognostic marker for some cancers.
Conclusions: The implementation of in silico SNP prioritization methods provides a great framework for the recognition of functional SNPs. The results obtained from the current study would be called laboratory investigations.
Keywords: Deleterious SNPs; HLA-G gene; In silico analysis; Missense mutation; Structural and functional impact.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Predicting the functional and structural consequences of nsSNPs in human methionine synthase gene using computational tools.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019 Aug;65(4):288-300. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2019.1568611. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019. PMID: 30676783
-
Investigating the functional and structural effect of non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 gene: An in-silico study.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 24;20(1):e0316465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316465. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39854591 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of deleterious single-nucleotide polymorphisms of human LYZ C gene: an in silico study.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2022 Jul 1;20(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s43141-022-00383-8. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35776277 Free PMC article.
-
Computational prediction of the effects of non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in human DNA repair genes.Neuroscience. 2007 Apr 14;145(4):1273-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.09.004. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17055652 Review.
-
Deciphering deleterious missense variants in the MC4R gene in the pathogenesis of obesity.Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2025 Apr;72(4):501559. doi: 10.1016/j.endien.2025.501559. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2025. PMID: 40221191 Review.
Cited by
-
HBD-2 variants and SARS-CoV-2: New insights into inter-individual susceptibility.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 9;13:1008463. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1008463. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36569842 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Mutation of the KLK6 Gene in a Family With Knee Osteoarthritis.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 11;12:784176. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.784176. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34858488 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of a novel TBC1D24 variation causing autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 27;14(1):4734. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55435-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38413761 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes and SNPs linked to harvest body weight of genetically improved rohu carp, Labeo rohita.Front Genet. 2023 Jun 8;14:1153911. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1153911. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37359361 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of mutations in porcine STAT5A that contributes to the transcription of CISH.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Jan 17;9:1090833. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1090833. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36733428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Group ISMW A map of human genome sequence variation containing 1.42 million single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nature. 2001;409(6822):928. - PubMed
-
- Ding C, Jin S. High-throughput methods for SNP genotyping. In: Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms. Springer, Methods Mol Biol. 2009;578:245–54. https://link.springer.com/protocol/10.1007/978-1-60327-411-1_16. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rajasekaran R, Doss CGP, Sudandiradoss C, Ramanathan K, Sethumadhavan R. In silico analysis of structural and functional consequences in p16INK4A by deleterious nsSNPs associated CDKN2A gene in malignant melanoma. Biochimie. 2008;90(10):1523–1529. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

