Identification and characterization of the bacteriocin Carocin S3 from the multiple bacteriocin producing strain of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum
- PMID: 32867691
- PMCID: PMC7461348
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-020-01955-9
Identification and characterization of the bacteriocin Carocin S3 from the multiple bacteriocin producing strain of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum
Abstract
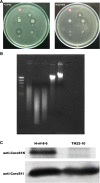
Background: Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family, which causes soft-rot disease in numerous plants worldwide resulting in significant economic losses. Results from our previous studies showed that the strain H-rif-8-6 produces low-molecular-weight bacteriocin (LMWB) Carocin S1. Interestingly, TH22-10, the caroS1K:Tn5 insertional mutant in H-rif-8-6, loses Carocin S1 producing ability, but still produces other LMWBs which the indicator strain SP33 can detect. The SP33 is one of the many strains that are sensitive toward the cytotoxic effects of Carocin S3K, but not Carocin S1. The result revealed that H-rif-8-6 is a multiple-bacteriocin producing strain.
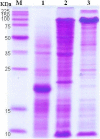
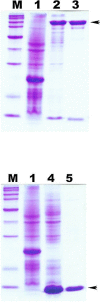
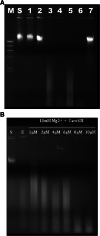
Results: In this study, a 4.1-kb DNA fragment was isolated from the chromosomal DNA of Pcc strain, H-rif-8-6, by a DNA probe using the caroS1K gene as the template. DNA sequencing and analysis by GenBank revealed two complete open reading frames (ORFs), designated ORF1 and ORF2, which were identified within the sequence fragment. ORF1 and ORF2, similar to the identified carocin S2 genes, encode the killer (Carocin S3K) and the immunity (Carocin S3I) proteins, respectively, which were homologous to the colicin E3 gene. Carocin S3K and Carocin S3I were expressed, isolated, and purified in Escherichia coli BL21 after subcloning of the expression plasmid pGS3KI or pGSK3I. SDS-PAGE analysis showed that the relative masses of Carocin S3K and Carocin S3I were 95.6 kDa and 10.2 kDa, respectively. The results reveal that Carocin S3K has higher antimicrobial and specific antimicrobial activities for Pcc along with a nuclease activity than Carocin S3I. However, Carocin S3I inhibits the activity of Carocin S3K. Interestingly, a high concentration of Carocin S3I protein is also a DNA nuclease, and Carocin S3K also inhibits its activity.
Conclusion: This study showed that another type of bacteriocin was found in Pectobacterium carotovorum. This new type of bacteriocin, Carocin S3, has the killer protein, Carocin S3K, and the immunity protein, Carocin S3I.
Keywords: Carocin S3; Low-molecular-weight Bacteriocin; Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

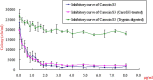
 ) and Carocin S3K:Carocin S3I in a molar ratio of 1:1 (
) and Carocin S3K:Carocin S3I in a molar ratio of 1:1 (  ). The effect of trypsin on the Carocin S3K was also assayed (
). The effect of trypsin on the Carocin S3K was also assayed (  ). The data are reported as means ± standard deviations
). The data are reported as means ± standard deviations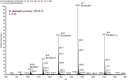

Similar articles
-
A Novel Deoxyribonuclease Low-Molecular-Weight Bacteriocin, Carocin S4, from Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum.Microorganisms. 2023 Jul 22;11(7):1854. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071854. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37513026 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, purification, and functional characterization of Carocin S2, a ribonuclease bacteriocin produced by Pectobacterium carotovorum.BMC Microbiol. 2011 May 12;11:99. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-99. BMC Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21569432 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and expression of the Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora gene encoding the low-molecular-weight bacteriocin carocin S1.J Bacteriol. 2007 Jan;189(2):620-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.01090-06. Epub 2006 Oct 27. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17071754 Free PMC article.
-
Injectisome T3SS subunits as potential chaperones in the extracellular export of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum bacteriocins Carocin S1 and Carocin S3 secreted via flagellar T3SS.BMC Microbiol. 2021 Dec 15;21(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02405-w. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34911446 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a new bacteriocin, Carocin D, from Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum Pcc21.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Nov;76(22):7541-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03103-09. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20870796 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Outer membrane translocation of pyocins via the copper regulated TonB-dependent transporter CrtA.Biochem J. 2023 Jul 26;480(14):1035-1049. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20220552. Biochem J. 2023. PMID: 37399084 Free PMC article.
-
Biocontrol of Soft Rot Caused by Pectobacterium odoriferum with Bacteriophage phiPccP-1 in Kimchi Cabbage.Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 8;9(4):779. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9040779. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33917817 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Uncharacterized Domain of Carocin S2: A Ribonuclease Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum Bacteriocin.Microorganisms. 2022 Feb 4;10(2):359. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020359. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35208813 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Deoxyribonuclease Low-Molecular-Weight Bacteriocin, Carocin S4, from Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum.Microorganisms. 2023 Jul 22;11(7):1854. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071854. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37513026 Free PMC article.
-
Unleashing the Influence of cAMP Receptor Protein: The Master Switch of Bacteriocin Export in Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 5;24(11):9752. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119752. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barras F, van Gijsegem F, Chatterjee AK. Extracellular enzymes and pathogenesis of soft-rot Erwinia. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 1994;32(1):201–234. doi: 10.1146/annurev.py.32.090194.001221. - DOI
-
- Chatterjee A, Dumenyo C, Liu Y, Chatterjee A. Erwinia: genetics of pathogenicity factors. In Encyclopedia of microbiology, 2nd ed. San Diego: Academic Press; 2000. p. 236-60.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

