Removal of Remdesivir's Metabolite GS-441524 by Hemodialysis in a Double Lung Transplant Recipient with COVID-19
- PMID: 32868327
- PMCID: PMC7577145
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01521-20
Removal of Remdesivir's Metabolite GS-441524 by Hemodialysis in a Double Lung Transplant Recipient with COVID-19
Abstract
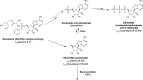
Remdesivir has reported efficacy against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in vitro and in vivo Drug-drug interactions limit therapeutic options in transplant patients. Remdesivir and its metabolite GS-441524 are excreted principally in urine. In intensive care unit (ICU) settings, in which multiple-organ dysfunctions can occur rapidly, hemodialysis may be a viable option for maintaining remdesivir treatment, while improving tolerance, by removing both remdesivir's metabolite (GS-441524) and sulfobutylether β-cyclodextrin sodium (SEBCD). Additional studies may prove informative, particularly in the evaluations of therapeutic options for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Keywords: hemodialysis; pharmacokinetics; remdesivir.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Reply to Yan and Muller, "Captisol and GS-704277, but Not GS-441524, Are Credible Mediators of Remdesivir's Nephrotoxicity".Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Nov 17;64(12):e01937-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01937-20. Print 2020 Nov 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32988815 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Captisol and GS-704277, but Not GS-441524, Are Credible Mediators of Remdesivir's Nephrotoxicity.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Nov 17;64(12):e01920-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01920-20. Print 2020 Nov 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32988821 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, Liu W, Wang J, Fan G, Ruan L, Song B, Cai Y, Wei M, Li X, Xia J, Chen N, Xiang J, Yu T, Bai T, Xie X, Zhang L, Li C, Yuan Y, Chen H, Li H, Huang H, Tu S, Gong F, Liu Y, Wei Y, Dong C, Zhou F, Gu X, Xu J, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Li H, Shang L, Wang K, Li K, Zhou X, Dong X, Qu Z, Lu S, Hu X, Ruan S, Luo S, Wu J, Peng L, Cheng F, Pan L, Zou J, Jia C, et al. . 2020. A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med 382:1787–1799. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avataneo V, de Nicolò A, Cusato J, Antonucci M, Manca A, Palermiti A, Waitt C, Walimbwa S, Lamorde M, di Perri G, D’Avolio A. 2020. Development and validation of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for quantification of the prodrug remdesivir and its metabolite GS-441524: a tool for clinical pharmacokinetics of SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 and Ebola virus disease. J Antimicrob Chemother 75:1772–1777. doi:10.1093/jac/dkaa152. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

