Rapid isothermal amplification and portable detection system for SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32868442
- PMCID: PMC7502724
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2014739117
Rapid isothermal amplification and portable detection system for SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
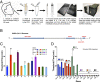
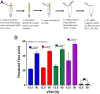
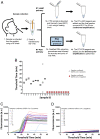
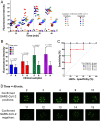
The COVID-19 pandemic provides an urgent example where a gap exists between availability of state-of-the-art diagnostics and current needs. As assay protocols and primer sequences become widely known, many laboratories perform diagnostic tests using methods such as RT-PCR or reverse transcription loop mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP). Here, we report an RT-LAMP isothermal assay for the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus and demonstrate the assay on clinical samples using a simple and accessible point-of-care (POC) instrument. We characterized the assay by dipping swabs into synthetic nasal fluid spiked with the virus, moving the swab to viral transport medium (VTM), and sampling a volume of the VTM to perform the RT-LAMP assay without an RNA extraction kit. The assay has a limit of detection (LOD) of 50 RNA copies per μL in the VTM solution within 30 min. We further demonstrate our assay by detecting SARS-CoV-2 viruses from 20 clinical samples. Finally, we demonstrate a portable and real-time POC device to detect SARS-CoV-2 from VTM samples using an additively manufactured three-dimensional cartridge and a smartphone-based reader. The POC system was tested using 10 clinical samples, and was able to detect SARS-CoV-2 from these clinical samples by distinguishing positive samples from negative samples after 30 min. The POC tests are in complete agreement with RT-PCR controls. This work demonstrates an alternative pathway for SARS-CoV-2 diagnostics that does not require conventional laboratory infrastructure, in settings where diagnosis is required at the point of sample collection.
Keywords: COVID-19 diagnostics; RT-LAMP; SARS-CoV-2; point-of-care; smartphone reader.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: W.P.K. is a cofounder and Chief Scientist at Fast Radius Inc., where the additively manufactured cartridge was produced. B.T.C. serves as a consultant to and has financial interests in Reliant Immune Diagnostics.
Figures

Update of
-
Rapid Isothermal Amplification and Portable Detection System for SARS-CoV-2.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 May 21:2020.05.21.108381. doi: 10.1101/2020.05.21.108381. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 15;117(37):22727-22735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014739117. PMID: 32511358 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- World Health Organization , Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) pandemic. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019. Accessed 20 May 2020.
-
- World Health Organization , Coronavirus Disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... Accessed 20 May 2020.
-
- World Health Organization , WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re.... Accessed 20 May 2020.
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services , “Hospital experiences responding to the COVID-19 pandemic: Results of a national pulse survey March 23–27, 2020” (Rep. OEI-06-20-00300, US Department of Health and Human Services, 2020).
-
- Ranoa D. R. E., et al., Saliva-based molecular testing for SARS-CoV-2 that bypasses RNA extraction. bioRxiv:10.1101/2020.06.18.159434 (18 June 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

