Automatically discriminating and localizing COVID-19 from community-acquired pneumonia on chest X-rays
- PMID: 32868956
- PMCID: PMC7448783
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107613
Automatically discriminating and localizing COVID-19 from community-acquired pneumonia on chest X-rays
Abstract
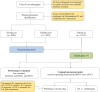
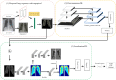
The COVID-19 outbreak continues to threaten the health and life of people worldwide. It is an immediate priority to develop and test a computer-aided detection (CAD) scheme based on deep learning (DL) to automatically localize and differentiate COVID-19 from community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) on chest X-rays. Therefore, this study aims to develop and test an efficient and accurate deep learning scheme that assists radiologists in automatically recognizing and localizing COVID-19. A retrospective chest X-ray image dataset was collected from open image data and the Xiangya Hospital, which was divided into a training group and a testing group. The proposed CAD framework is composed of two steps with DLs: the Discrimination-DL and the Localization-DL. The first DL was developed to extract lung features from chest X-ray radiographs for COVID-19 discrimination and trained using 3548 chest X-ray radiographs. The second DL was trained with 406-pixel patches and applied to the recognized X-ray radiographs to localize and assign them into the left lung, right lung or bipulmonary. X-ray radiographs of CAP and healthy controls were enrolled to evaluate the robustness of the model. Compared to the radiologists' discrimination and localization results, the accuracy of COVID-19 discrimination using the Discrimination-DL yielded 98.71%, while the accuracy of localization using the Localization-DL was 93.03%. This work represents the feasibility of using a novel deep learning-based CAD scheme to efficiently and accurately distinguish COVID-19 from CAP and detect localization with high accuracy and agreement with radiologists.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chest X-ray (CXR); Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP); Computer-aided detection (CAD); Deep learning (DL).
© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Li Q., Guan X., Wu P., Wang X., Zhou L., Tong Y., Ren R., Leung K.S., Lau E.H., Wong J.Y., Xing X., Xiang N., Wu Y., Li C., Chen Q., Li D., Liu T., Zhao J., Liu M., Tu W., Chen C., Jin L., Yang R., Wang Q., Zhou S., Wang R., Liu H., Luo Y., Liu Y., Shao G., Li H., Tao Z., Yang Y., Deng Z., Liu B., Ma Z., Zhang Y., Shi G., Lam T.T., Wu J.T., Gao G.F., Cowling B.J., Yang B., Leung G.M., Feng Z. Early transmission dynamics in wuhan, china, of novel coronavirus infected pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382(13):1199–1207. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
