Lymph Liquid Biopsy for Detection of Cancer Stem Cells
- PMID: 32869909
- PMCID: PMC9237844
- DOI: 10.1002/cyto.a.24221
Lymph Liquid Biopsy for Detection of Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
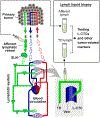
Collection of a blood sample defined by the term "blood liquid biopsy" is commonly used to detect diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic decision-making markers of metastatic tumors including circulating tumor cells (CTCs). Many tumors also release CTCs and other markers into lymph fluid, but the utility of lymphatic markers largely remains unexplored. Here, we introduce lymph liquid biopsy through collection of peripheral (afferent) and central (thoracic duct [TD]) lymph samples and demonstrates its feasibility for detection of stem-like CTCs potentially responsible for metastasis development and tumor relapse. Stemness of lymphatic CTCs (L-CTCs) was determined by spheroid-forming assay in vitro. Simultaneously, we tested blood CTCs by conventional blood liquid biopsy, and monitored the primary tumor size, early metastasis in a sentinel lymph node (SLN) and distant metastasis in lungs. Using a mouse model at early melanoma stage with no distant metastasis, we identified stem-like L-CTCs in lymph samples from afferent lymphatic vessels. Since these vessels transport cells from the primary tumor to SLN, our finding emphasizes the significance of the lymphatic pathway in development of SLN metastasis. Surprisingly, in pre-metastatic disease, stem-like L-CTCs were detected in lymph samples from the TD, which directly empties lymph into blood circulation. This suggests a new contribution of the lymphatic system to initiation of distant metastasis. Integration of lymph and blood liquid biopsies demonstrated that all mice with early melanoma had stem-like CTCs in at least one of three samples (afferent lymph, TD lymph, and blood). At the stage of distant metastasis, spheroid-forming L-CTCs were detected in TD lymph, but not in afferent lymph. Altogether, our results demonstrated that lymph liquid biopsy and testing L-CTCs holds promise for diagnosis and prognosis of early metastasis. © 2020 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
Keywords: metastasis circulating tumor cells cancer stem cells central thoracic duct lymph peripheral afferent lymphlymph liquid biopsy.
© 2020 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Vladimir Zharov, Ekaterina Galanzha, and UAMS have a financial interest in the Technology discussed in this publication. Dr. Vladimir Zharov has a financial interest in Cyto-Astra, LLC, which has licensed the Technology. These financial interests have been reviewed and approved in accordance with the UAMS conflict of interest policies.
Figures



References
-
- Pantel K, Alix-Panabières C. Liquid biopsy and minimal residual disease — Latest advances and implications for cure. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2019;16:409–424. - PubMed
-
- Dive C, Brady G. SnapShot: Circulating tumor cells. Cell 2017;168:742–742, 742.e1. - PubMed
-
- Rolfo C, Russo A. Liquid biopsy for early stage lung cancer moves ever closer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2020;9:517–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

