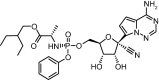
Remdesivir: First Approval
- PMID: 32870481
- PMCID: PMC7459246
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-020-01378-w
Remdesivir: First Approval
Abstract
The antiviral agent remdesivir (Veklury®; Gilead Sciences), nucleotide analogue prodrug, has broad-spectrum activity against viruses from several families. Having demonstrated potent antiviral activity against coronaviruses in preclinical studies, remdesivir emerged as a candidate drug for the treatment of the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, during the current global pandemic. Phase III evaluation of remdesivir in the treatment of COVID-19 commenced in early 2020 and has thus far yielded promising results. In late May 2020, Taiwan conditionally approved the use of remdesivir in patients with severe COVID-19. This was followed by a rapid succession of conditional approvals in various countries/regions including the EU and Canada. Preceding these conditional approvals, an emergency use authorization for remdesivir had been granted in the USA (on 1 May 2020) and a special approval for emergency use was granted in Japan (on 7 May 2020). This article summarizes the milestones in the development of remdesivir leading to its first conditional approval for the treatment of COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
Yvette Lamb is a salaried employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to the review and are responsible for the article content.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous