Antihypoxic oxygenation agents with respiratory hyperoxia to improve cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 32870821
- PMCID: PMC7598059
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI137554
Antihypoxic oxygenation agents with respiratory hyperoxia to improve cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
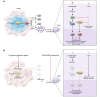
Hypoxia/HIF-1α- and extracellular adenosine/A2 adenosine receptor-mediated immunosuppression protects tissues from collateral damage by antipathogen immune cells. However, this mechanism also protects cancerous tissues by inhibiting antitumor immune cells in hypoxic and extracellular adenosine-rich tumors that are the most resistant to current therapies. Here, we explain a potentially novel, antiimmunosuppressive reasoning to justify strategies using respiratory hyperoxia and oxygenation agents in cancer treatment. Earlier attempts to use oxygenation of tumors as a monotherapy or to improve radiotherapy have failed because oxygenation protocols were not combined with immunotherapies of cancer. In contrast, the proposal for therapeutic use of antihypoxic oxygenation described here was motivated by the need to prevent the hypoxia/HIF-1α-driven accumulation of extracellular adenosine to (a) unleash antitumor immune cells from inhibition by intracellular cAMP and (b) prevent immunosuppressive transcription of cAMP response element- and hypoxia response element-containing immunosuppressive gene products (e.g., TGF-β). Use of oxygenation agents together with inhibitors of the A2A adenosine receptor may be required to enable the most effective cancer immunotherapy. The emerging outcomes of clinical trials of cancer patients refractory to all other treatments provide support for the molecular and immunological mechanism-based approach to cancer immunotherapy described here.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanistic Justifications of Systemic Therapeutic Oxygenation of Tumors to Weaken the Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1α-Mediated Immunosuppression.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1136:113-121. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-12734-3_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31201720 Review.
-
Immunological mechanisms of the antitumor effects of supplemental oxygenation.Sci Transl Med. 2015 Mar 4;7(277):277ra30. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa1260. Sci Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25739764 Free PMC article.
-
A2A adenosine receptor antagonists to weaken the hypoxia-HIF-1α driven immunosuppression and improve immunotherapies of cancer.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2016 Aug;29:90-6. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2016.06.009. Epub 2016 Jul 17. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27429212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic oxygenation weakens the hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor 1α-dependent and extracellular adenosine-mediated tumor protection.J Mol Med (Berl). 2014 Dec;92(12):1283-92. doi: 10.1007/s00109-014-1189-3. Epub 2014 Aug 15. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014. PMID: 25120128 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygenation and A2AR blockade to eliminate hypoxia/HIF-1α-adenosinergic immunosuppressive axis and improve cancer immunotherapy.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2020 Aug;53:84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Aug 22. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32841869 Review.
Cited by
-
HIF inhibitor 32-134D eradicates murine hepatocellular carcinoma in combination with anti-PD1 therapy.J Clin Invest. 2022 May 2;132(9):e156774. doi: 10.1172/JCI156774. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35499076 Free PMC article.
-
The role of DLL1 in long-term vascular normalization and cancer immunotherapy.Cancer Biol Med. 2021 Oct 29;18(4):940-3. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2021.0507. Cancer Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34708998 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A2AR eGFP reporter mouse enables elucidation of A2AR expression dynamics during anti-tumor immune responses.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 1;14(1):6990. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42734-0. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37914685 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in molecular pathology and therapy of non-small cell lung cancer.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jun 15;10(1):186. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02243-6. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40517166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia signaling in cancer: Implications for therapeutic interventions.MedComm (2020). 2023 Jan 23;4(1):e203. doi: 10.1002/mco2.203. eCollection 2023 Feb. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 36703877 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sitkovsky MV. Lessons from the A2A adenosine receptor antagonist-enabled tumor regression and survival in patients with treatment-refractory renal cell cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020;10(1):16–19. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-1280. - DOI - PubMed

