The effects of liraglutide and dapagliflozin on cardiac function and structure in a multi-hit mouse model of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- PMID: 32871009
- PMCID: PMC8318109
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa256
The effects of liraglutide and dapagliflozin on cardiac function and structure in a multi-hit mouse model of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
Abstract
Aims: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a multifactorial disease that constitutes several distinct phenotypes, including a common cardiometabolic phenotype with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Treatment options for HFpEF are limited, and development of novel therapeutics is hindered by the paucity of suitable preclinical HFpEF models that recapitulate the complexity of human HFpEF. Metabolic drugs, like glucagon-like peptide receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) and sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i), have emerged as promising drugs to restore metabolic perturbations and may have value in the treatment of the cardiometabolic HFpEF phenotype. We aimed to develop a multifactorial HFpEF mouse model that closely resembles the cardiometabolic HFpEF phenotype, and evaluated the GLP-1 RA liraglutide (Lira) and the SGLT2i dapagliflozin (Dapa).
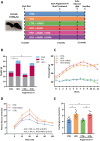
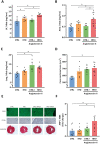
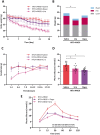
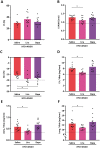
Methods and results: Aged (18-22 months old) female C57BL/6J mice were fed a standardized chow (CTRL) or high-fat diet (HFD) for 12 weeks. After 8 weeks HFD, angiotensin II (ANGII), was administered for 4 weeks via osmotic mini pumps. HFD + ANGII resulted in a cardiometabolic HFpEF phenotype, including obesity, impaired glucose handling, and metabolic dysregulation with inflammation. The multiple hit resulted in typical clinical HFpEF features, including cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis with preserved fractional shortening but with impaired myocardial deformation, atrial enlargement, lung congestion, and elevated blood pressures. Treatment with Lira attenuated the cardiometabolic dysregulation and improved cardiac function, with reduced cardiac hypertrophy, less myocardial fibrosis, and attenuation of atrial weight, natriuretic peptide levels, and lung congestion. Dapa treatment improved glucose handling, but had mild effects on the HFpEF phenotype.
Conclusions: We developed a mouse model that recapitulates the human HFpEF disease, providing a novel opportunity to study disease pathogenesis and the development of enhanced therapeutic approaches. We furthermore show that attenuation of cardiometabolic dysregulation may represent a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of HFpEF.
Keywords: Cardiometabolic; Dapagliflozin; HFpEF; Liraglutide; Mouse model.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Cardiometabolic phenotype of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction as a target of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists.Cardiovasc Res. 2021 Jul 27;117(9):1992-1994. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa334. Cardiovasc Res. 2021. PMID: 33231613 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, Falk V, González-Juanatey JR, Harjola VP, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GMC, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, Van Der Meer P.. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 2016;37:2129–2200. - PubMed
-
- Dunlay SM, Roger VL, Redfield MM.. Epidemiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat Rev Cardiol 2017;14:591–602. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Delling FN, Deo R, De Ferranti SD, Ferguson JF, Fornage M, Gillespie C, Isasi CR, Jiménez MC, Jordan LC, Judd SE, Lackland D, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth L, Liu S, Longenecker CT, Lutsey PL, MacKey JS, Matchar DB, Matsushita K, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, O’Flaherty M, Palaniappan LP, Pandey A, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Ritchey MD, Rodriguez CJ, Roth GA, Rosamond WD, Sampson UKA, Satou GM, Shah SH, Spartano NL, Tirschwell DL, Tsao CW, Voeks JH, Willey JZ, Wilkins JT, Wu JH, Alger HM, Wong SS, Muntner P.. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017;135:E67–E492. - PubMed
-
- Ho JE, Enserro D, Brouwers FP, Kizer JR, Shah SJ, Psaty BM, Bartz TM, Santhanakrishnan R, Lee DS, Chan C, Liu K, Blaha MJ, Hillege HL, van der Harst P, van Gilst WH, Kop WJ, Gansevoort RT, Vasan RS, Gardin JM, Levy D, Gottdiener JS, de Boer RA, Larson MG.. Predicting heart failure with preserved and reduced ejection fraction clinical perspective. Circ Hear Fail 2016;9:e003116. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

