Impact of first-wave COronaVIrus disease 2019 infection in patients on haemoDIALysis in Alsace: the observational COVIDIAL study
- PMID: 32871594
- PMCID: PMC7499735
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa170
Impact of first-wave COronaVIrus disease 2019 infection in patients on haemoDIALysis in Alsace: the observational COVIDIAL study
Abstract
Background: There are only scarce data regarding the presentation, incidence, severity and outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in patients undergoing long-term haemodialysis (HD). A prospective observational study was conducted in eight HD facilities in Alsace, France, to identify clinical characteristics of HD patients with COVID-19 and to assess the determinants of the risk of death.
Methods: All HD patients tested positive for COVID-19 from 5 March to 28 April 2020 were included. Collected data included patient characteristics, clinical features at diagnosis, laboratory data, treatments and outcomes.
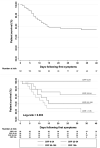
Results: Among 1346 HD patients, 123 tested positive for COVID-19. Patients had a median age of 77 years (interquartile range 66-83), with a high number of comorbidities (3.2 ± 1.6 per patient). Symptoms were compatible in 63% of patients. Asthenia (77%), diarrhoea (34%) and anorexia (32%) were frequent at diagnosis. The delay between the onset of symptoms and diagnosis, death or complete recovery was 2 (0-5), 7 (4-11) and 32 (26.5-35) days, respectively. Treatment, including lopinavir/ritonavir, hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroids, was administered in 23% of patients. The median C-reactive protein (CRP) and lymphocyte count at diagnosis was 55 mg/L (IQR 25-106) and 690 Ly/µL (IQR 450-960), respectively. The case fatality rate was 24% and determinants associated with the risk of death were body temperature {hazard ratio [HR] 1.96 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.11-3.44]; P = 0.02} and CRP at diagnosis [HR 1.01 (95% CI 1.005-1.017); P < 0.0001].
Conclusions: HD patients were found to be at high risk of developing COVID-19 and exhibited a high rate of mortality. While patients presented severe forms of the disease, they often displayed atypical symptoms, with the CRP level being highly associated with the risk of death.
Keywords: COVID-19; epidemiology; haemodialysis; mortality.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Scarpioni R, Manini A, Valsania T. et al. Covid-19 and its impact on nephropathic patients: the experience at Ospedale “Guglielmo da Saliceto” in Piacenza. G Ital Nefrol 2020; 37: 2020-vol2. Doi: 10.1126/science.abc3517 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous