Taxonomy of Echinostoma revolutum and 37-Collar-Spined Echinostoma spp.: A Historical Review
- PMID: 32871630
- PMCID: PMC7462802
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2020.58.4.343
Taxonomy of Echinostoma revolutum and 37-Collar-Spined Echinostoma spp.: A Historical Review
Abstract
Echinostoma flukes armed with 37 collar spines on their head collar are called as 37-collar-spined Echinostoma spp. (group) or 'Echinostoma revolutum group'. At least 56 nominal species have been described in this group. However, many of them were morphologically close to and difficult to distinguish from the other, thus synonymized with the others. However, some of the synonymies were disagreed by other researchers, and taxonomic debates have been continued. Fortunately, recent development of molecular techniques, in particular, sequencing of the mitochondrial (nad1 and cox1) and nuclear genes (ITS region; ITS1-5.8S-ITS2), has enabled us to obtain highly useful data on phylogenetic relationships of these 37-collar-spined Echinostoma spp. Thus, 16 different species are currently acknowledged to be valid worldwide, which include E. revolutum, E. bolschewense, E. caproni, E. cinetorchis, E. deserticum, E. lindoense, E. luisreyi, E. mekongi, E. miyagawai, E. nasincovae, E. novaezealandense, E. paraensei, E. paraulum, E. robustum, E. trivolvis, and Echinostoma sp. IG of Georgieva et al., 2013. The validity of the other 10 species is retained until further evaluation, including molecular analyses; E. acuticauda, E. barbosai, E. chloephagae, E. echinatum, E. jurini, E. nudicaudatum, E. parvocirrus, E. pinnicaudatum, E. ralli, and E. rodriguesi. In this review, the history of discovery and taxonomic debates on these 26 valid or validity-retained species are briefly reviewed.
Keywords: 37-collar-spined echinostome; Echinostoma; Echinostoma revolutum; historical review; ‘revolutum’ group.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflict of interest related to this study.
Figures
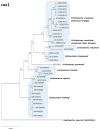
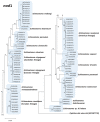
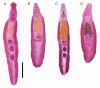
References
-
- Yamaguti S. Synopsis of digenetic trematodes of vertebrates. I. Tokyo, Japan: Keigaku Publishing Co; 1971. pp. 1–1074.
-
- Chai JY. Echinostomes in humans. In: Fried B, Toledo R, editors. The Biology of Echinostomes. New York, USA: Springer; 2009. pp. 147–183.
-
- Chai JY. Echinostomes. The Netherlands: Springer Nature B; 2019. Human Intestinal Flukes. Chapter 2; pp. 169–343.
-
- Kanev I. Life-cycle, delimitation and redescription of Echinostoma revolutum (Froelich, 1802) (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) Syst Parasitol. 1994;28:125–144.
-
- Kanev I, Dimitrov V, Radev V, Fried B. Redescription of Echinostoma jurini (Skvortzov, 1924) with a discussion of its identity and characteristics. Ann Naturhist Mus Wien. 1995;97B:37–53.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

