Immobilisation and Release of Radical Scavengers on Nanoclays for Chemical Reinforcement of Proton Exchange Membranes
- PMID: 32872314
- PMCID: PMC7559798
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes10090208
Immobilisation and Release of Radical Scavengers on Nanoclays for Chemical Reinforcement of Proton Exchange Membranes
Abstract
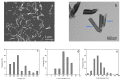
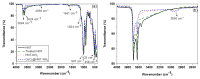
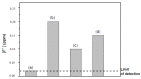
Mechanical and chemical stability of proton exchange membranes are crucial requirements for the development of fuel cells for durable energy conversion. To tackle this challenge, bi-functional nanoclays grafted with amino groups and with embedded radical scavengers, that is, CeO2 nanoparticles were incorporated into Aquivion® ionomer. The composite membranes presented high proton conductivity and increased stability to radical attack compared to non-modified Aquivion membranes, demonstrating the effectiveness of the approach based on radical scavenger immobilisation and release from clay nanocontainers.
Keywords: cerium oxide; halloysite; proton exchange membrane fuel cells; radical scavengers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
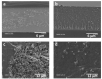
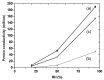
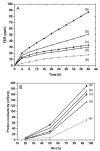
References
-
- De Bruijn F.A., Dam V.A.T., Janssen G.J.M. Review: Durability and degradation issues of PEM fuel cell components. Fuel Cells. 2008;8:3–22. doi: 10.1002/fuce.200700053. - DOI
-
- [(accessed on 15 June 2020)]; Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/doe-technical-targets-fuel-cell-sy....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

