The Possible Contribution of P-Glycoprotein in the Protective Effect of Paeonol against Methotrexate-Induced Testicular Injury in Rats
- PMID: 32872504
- PMCID: PMC7558391
- DOI: 10.3390/ph13090223
The Possible Contribution of P-Glycoprotein in the Protective Effect of Paeonol against Methotrexate-Induced Testicular Injury in Rats
Abstract
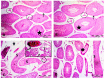
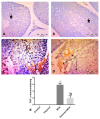
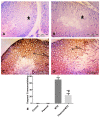
Paeonol, a phenolic ingredient in the genus Paeonia, possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Methotrexate (MTX) is a commonly used chemotherapeutic agent; however, its germ cell damage is a critical problem. P-glycoprotein (P-gp), an efflux transporter, is a member of the blood-testis barrier. The present study evaluated the protective effect of paeonol on MTX-induced testicular injury in rats with the exploration of its mechanism and the possible contribution of P-gp in such protection. Testicular weight, serum testosterone, and testicular P-gp levels were measured. Testicular oxidant/antioxidant status was evaluated via determining the levels of malondialdehyde, total nitrite, reduced glutathione, and superoxide dismutase activity. The inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and the apoptotic marker caspase 3 were estimated immunohistochemically. Testicular histopathology and spermatogenesis scores were also examined. MTX caused histopathologically evident testicular damage with decreased testicular weight, testosterone level, and spermatogenesis score, as well as significant increases in oxidative, inflammatory, and apoptotic responses. Paeonol significantly restored testicular weight, testosterone level, spermatogenesis score, and oxidant/antioxidant balance. Moreover, paeonol increased the testicular P-gp level and significantly decreased TNF-α and caspase 3 immunostaining. In conclusion, paeonol offered a protective effect against MTX-induced testicular injury through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic effects, as well as by increasing testicular P-gp level.
Keywords: P-glycoprotein; caspase 3; methotrexate; oxidative stress; paeonol; testicular injury; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Paeonol Attenuates Methotrexate-Induced Cardiac Toxicity in Rats by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Suppressing TLR4-Induced NF-κB Inflammatory Pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Feb 10;2020:8641026. doi: 10.1155/2020/8641026. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32104151 Free PMC article.
-
Paeonol protects against testicular ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats through inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation.Andrologia. 2020 Jul;52(6):e13599. doi: 10.1111/and.13599. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Andrologia. 2020. PMID: 32314822
-
Paeonol Protects Against Methotrexate-Induced Nephrotoxicity via Upregulation of P-gp Expression and Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 4;13:774387. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.774387. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35185559 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effects of alpha lipoic acid on methotrexate induced testis injury in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:1486-1492. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.078. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29793311
-
Paeonol for the Treatment of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Pharmacological and Mechanistic Overview.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jul 21;8:690116. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.690116. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34368250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Paeonol Protects against Methotrexate Hepatotoxicity by Repressing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis-The Role of Drug Efflux Transporters.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 21;15(10):1296. doi: 10.3390/ph15101296. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297408 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Antidiabetic Activity of Methanolic Extract of Punica granatum Leaves in Nicotinamide/Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes in Rats.Plants (Basel). 2020 Nov 19;9(11):1609. doi: 10.3390/plants9111609. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33228177 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet Rich Plasma and Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mitigate Methotrexate-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rat via Nrf2/Pparγ/HO-1 and NF-Κb/Keap1/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathways: Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Interplay.Toxics. 2023 Apr 22;11(5):398. doi: 10.3390/toxics11050398. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37235213 Free PMC article.
-
Zygo-Albuside A: New Saponin from Zygophyllum album L. with Significant Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Antiapoptotic Effects against Methotrexate-Induced Testicular Damage.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 16;23(18):10799. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810799. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142712 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric and visual analysis of blood-testis barrier research.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 22;13:969257. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.969257. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36071829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Taher A.Y., Morsy M.A., Rifaai R.A., Zenhom N.M., Abdel-Gaber S.A. Paeonol Attenuates Methotrexate-Induced Cardiac Toxicity in Rats by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Suppressing TLR4-Induced NF-κB Inflammatory Pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020;2020:8641026. doi: 10.1155/2020/8641026. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

