A Window of Vascular Plasticity Coupled to Behavioral Recovery after Stroke
- PMID: 32873722
- PMCID: PMC7531554
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1464-20.2020
A Window of Vascular Plasticity Coupled to Behavioral Recovery after Stroke
Abstract
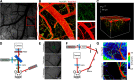
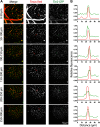
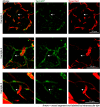
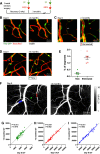
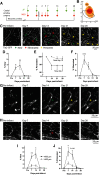
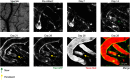
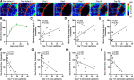
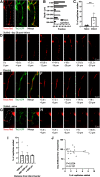
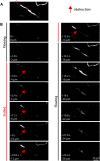
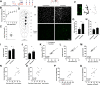
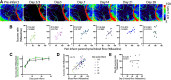
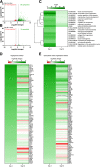
Stroke causes remodeling of vasculature surrounding the infarct, but whether and how vascular remodeling contributes to recovery are unclear. We established an approach to monitor and compare changes in vascular structure and blood flow with high spatiotemporal precision after photothrombotic infarcts in motor cortex using longitudinal 2-photon and multiexposure speckle imaging in mice of both sexes. A spatially graded pattern of vascular structural remodeling in peri-infarct cortex unfolded over the first 2 weeks after stroke, characterized by vessel loss and formation, and selective stabilization of a subset of new vessels. This vascular structural plasticity was coincident with transient activation of transcriptional programs relevant for vascular remodeling, reestablishment of peri-infarct blood flow, and large improvements in motor performance. Local vascular plasticity was strongly predictive of restoration of blood flow, which was in turn predictive of behavioral recovery. These findings reveal the spatiotemporal evolution of vascular remodeling after stroke and demonstrate that a window of heightened vascular plasticity is coupled to the reestablishment of blood flow and behavioral recovery. Our findings support that neovascularization contributes to behavioral recovery after stroke by restoring blood flow to peri-infarct regions. These findings may inform strategies for enhancing recovery from stroke and other types of brain injury.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT An improved understanding of neural repair could inform strategies for enhancing recovery from stroke and other types of brain injury. Stroke causes remodeling of vasculature surrounding the lesion, but whether and how the process of vascular remodeling contributes to recovery of behavioral function have been unclear. Here we used longitudinal in vivo imaging to track vascular structure and blood flow in residual peri-infarct cortex after ischemic stroke in mice. We found that stroke created a restricted period of heightened vascular plasticity that was associated with restoration of blood flow, which was in turn predictive of recovery of motor function. Therefore, our findings support that vascular remodeling facilitates behavioral recovery after stroke by restoring blood flow to peri-infarct cortex.
Keywords: angiogenesis; blood flow; in vivo imaging; neural repair; recovery; vascular remodeling.
Copyright © 2020 the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reactive astrocytes facilitate vascular repair and remodeling after stroke.Cell Rep. 2021 Apr 27;35(4):109048. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109048. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 33910014 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitative Training Interacts with Ischemia-Instigated Spine Dynamics to Promote a Lasting Population of New Synapses in Peri-Infarct Motor Cortex.J Neurosci. 2019 Oct 23;39(43):8471-8483. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1141-19.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 11. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31511430 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes augments in vivo microvascular blood flow dynamics after stroke.J Neurosci. 2013 Dec 4;33(49):19194-204. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3513-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24305815 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear medicine in the rehabilitative treatment evaluation in stroke recovery. Role of diaschisis resolution and cerebral reorganization.Eura Medicophys. 2007 Jun;43(2):221-39. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Eura Medicophys. 2007. PMID: 17268387 Review.
-
Integrated technology for evaluation of brain function and neural plasticity.Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2004 Feb;15(1):263-306. doi: 10.1016/s1047-9651(03)00124-4. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2004. PMID: 15029909 Review.
Cited by
-
Corrigendum to "Platelets and Hemostatic Proteins are Co-Localized with Chronic Neuroinflammation Surrounding Implanted Intracortical Microelectrodes" [Acta Biomaterialia. Volume 166, August 2023, Pages 278-290].Acta Biomater. 2024 Jul 1;182:303-308. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.05.039. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Acta Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38845260 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Liver-secreted fluorescent blood plasma markers enable chronic imaging of the microcirculation.Cell Rep Methods. 2022 Sep 21;2(10):100302. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100302. eCollection 2022 Oct 24. Cell Rep Methods. 2022. PMID: 36313804 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity Modulation and Clinical Efficacy of Acupuncture for Posterior Circulation Infarction Vertigo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 28;2022:3740856. doi: 10.1155/2022/3740856. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35800002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Recovery Caused by Human Adipose Tissue Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Administered 24 h after Stroke in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 28;22(23):12860. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312860. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884665 Free PMC article.
-
Platelets and hemostatic proteins are co-localized with chronic neuroinflammation surrounding implanted intracortical microelectrodes.Acta Biomater. 2023 Aug;166:278-290. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.05.004. Epub 2023 May 19. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37211307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown CE, Aminoltejari K, Erb H, Winship IR, Murphy TH (2009) In vivo voltage-sensitive dye imaging in adult mice reveals that somatosensory maps lost to stroke are replaced over weeks by new structural and functional circuits with prolonged modes of activation within both the peri-infarct zone and distant sites. J Neurosci 29:1719–1734. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4249-08.2009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
